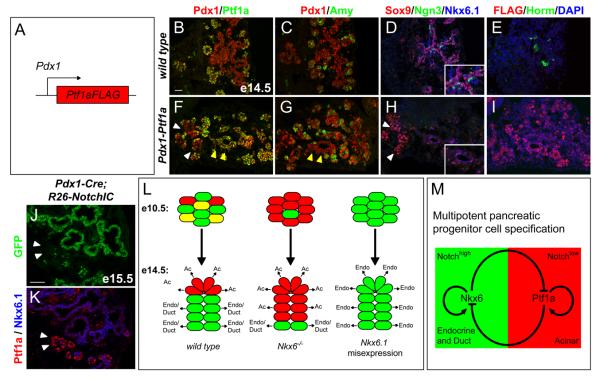
Figure 4. Ptf1a is a repressor of endocrine fate.
(A) Schematic of the Pdx1-Ptf1a transgene. (B-I) Immunofluorescence staining of adjacent pancreas sections from e14.5 embryos shows ectopic expression of Ptf1a (F) and FLAG (I) in the trunk region of Pdx1-Ptf1a embryos. Ptf1a misexpression does not uniformly induce amylase expression (yellow arrow heads, F,G). Ectopic Ptf1a represses Nkx6.1, Sox9 and Ngn3 (H), and prevents endocrine cell differentiation (I). White arrowheads in (F,H) point to a region that does not misexpress Ptf1a and therefore expresses Sox9 and Nkx6.1 (H). Insets in (D,H) show higher magnifications. (J) Summary of the observed cell fate changes in Nkx6 loss- and gain-of-function models. (K,L) Immunofluorescence staining of adjacent pancreatic sections from Pdx1-Cre(mosaic);R26NotchIC embryos at e15.5 shows expression of Nkx6.1 in all cells that have recombined the R26NotchIC allele and therefore activated NotchIC/GFP expression. Ptf1a is excluded from the GFP+ domain, but is expressed in areas that have not recombined the R26NotchIC allele (arrowheads, K,L). (M) Our data support a model whereby a regulatory circuit comprised of the counter-antagonistic repressive activities of Nkx6 and Ptf1a restricts multipotent pancreatic progenitors to ductal/endocrine and acinar fates, respectively. Positive autoregulatory feedback of Nkx6 and Ptf1a creates bistability of the fate choice. High Notch activity appears to favor the Nkx6.1+ state. Note, for simplicity the redundant factors Nkx6.1 and Nkx6.2 are referred to as Nkx6. Scale bar=50 μm; Amy, amylase; Horm, hormone (insulin, glucagon, somatostatin, pancreatic polypeptide), Endo, endocrine; Ac, acinar.