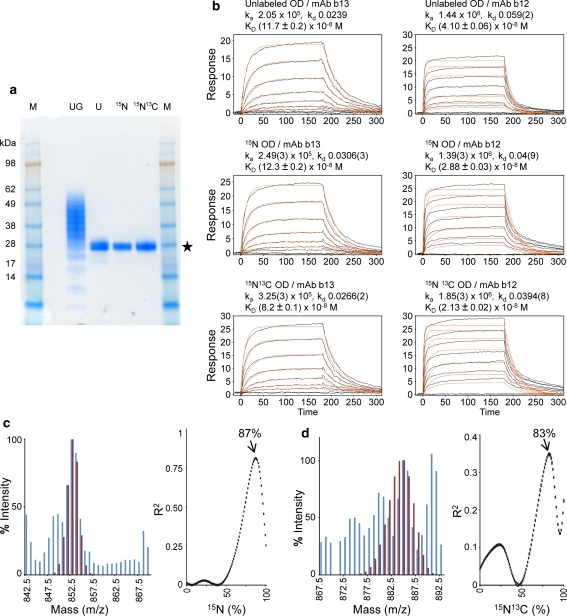
Fig. 2.
Characterization of isotopically enriched HIV-1 gp120 Outer domain expressed using the adenoviral expression system. Production of isotopically enriched correctly folded post-translationally modified proteins is feasible using the adenoviral expression system. a SDS–PAGE analysis of the HIV-1 gp120 outer domain. Lane UG glycosylated outer domain demonstrates the micro heterogeneity observed in the glycans, Lanes U, 15N,15N13C deglycosylation of unlabeled, 15N, 15N/13C labeled gp120 outer domain with Endoglycosidase H resulted in a 28 kDa deglycosylated protein that was used for biophysical measurements (gel filtration profiles are shown in Fig. S6). Lane M Molecular weight markers. b Surface plasmon resonance analysis of deglycosylated unlabeled, 15N and 15N/13C labeled binding to monoclonal antibodies b12 and b13 demonstrates that the expressed protein is correctly folded and biologically active. c Mass spectral analysis of a tryptic peptide fragment TIIVQLR used to determine % incorporation of 15N. A comparison of experimental (blue histogram) and computed (maroon histogram) pattern for 87% incorporation of 15N is shown (left panel). The correlation between observed experimental pattern and computed patterns are shown for each percentage incorporation of 15N. d Mass spectral analysis of a tryptic peptide TIIVQLR to determine % incorporation of 13C. A comparison of experimental (blue histogram) and computed (maroon histogram) pattern for 84% incorporation of 13C is shown (left panel). Although the maximum of the correlation for 13C incorporation is at 83%, the best fit of the experimental and computational 13C incorporation was estimated to be 84%, which allows the highest computational peak to match one of the experimentally-observed modes (see “Supplementary methods”). The correlations between observed experimental pattern and computed patterns are shown for each percentage incorporation of 13C with a fixed 15N incorporation of 84% (right panel)