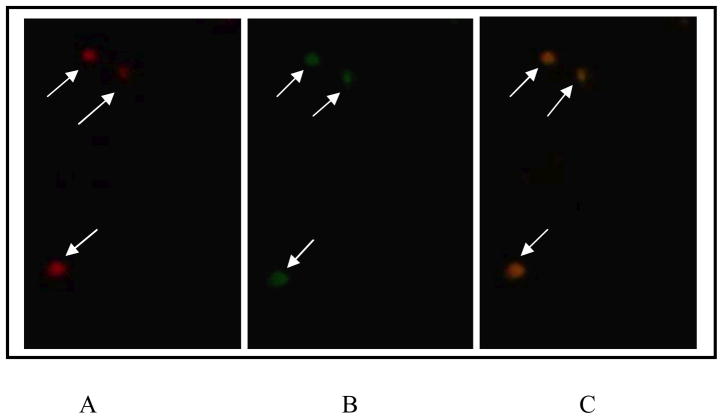
Fig. 2.
Detection of P. gingivalis in carotid atheromatous tissue sections using double immunohistofluorescence and two different antibodies. Images are representative; three separate slides yielded similar results.
A, Primary antibody, mouse anti-P. gingivalis IgG1 monoclonal antibody 61BG1.3; secondary antibody, Alexa Fluor 456-conjugated goat anti-mouse antibody (red).
B, Primary antibody, rabbit anti-P. gingivalis serum; secondary antibody, goat anti-rabbit Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated antibody (green).
C, Colocalization of both stains is represented as overlap of the preceding images.
Negative controls (not shown): primary mouse unrelated IgG1 isotype control antibody and primary rabbit antibody (omitted). Scale bar, 10 μm.