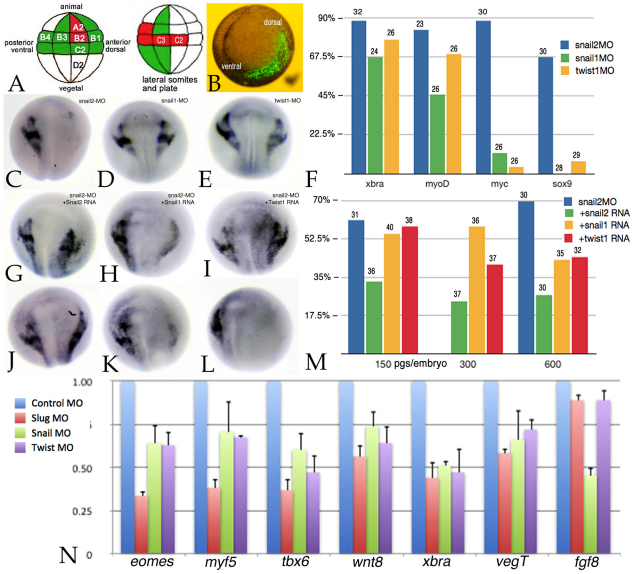
Fig. 4.
Target blastomere injection effects. (A) Fate map of the 32-cell X. laevis embryo, lateral to front, with blastomeres marked with respect to tiers (A-D) and position (1, dorsal; 4, ventral). Blastomeres are marked that make a major (red) or moderate (green) contribution to neural crest (left) or to lateral somites and plate mesoderm (right). (B) At the 32-cell stage, this embryo was injected with RNA encoding GFP; the embryo was photographed under bright-field and epifluorescence illumination at stage 11. Ventral pole to front (dorsal and ventral are marked). (C-E) C2/C3 blastomeres were injected with snail2, snail1 or twist1 MOs; at stage 17/18 the embryos were fixed and stained in situ for sox9 RNA. sox9 expression was lost in snail2 morphant embryos (C), but was present in snail1 (D) and twist1 (E) morphants. (F) The phenotypes of C2/C3 morphant embryos with respect to xbra, myoD, c-myc and sox9 expression. Bars indicate percentage loss of expression; the number of embryos is indicated above each bar. (G-I) The effects of the snail2 MO could be partially rescued by injection of high levels (600 pg/embryo) of snail2 (G), snail1 (H) or twist1(I) RNAs. (J-L) snail2 RNA was more effective at rescuing the snail2 C2/C3 morphant sox9 phenotype than either snail1 or twist1 RNAs. snail2 C2/C3 morphant embryos were co-injected with 150 pg/embryo of snail2 (J), snail1 (K) or twist1 (L) RNA. (M) The rescue of the C2/C3 snail2 morphant sox9 phenotype by 150, 300 and 600 pg/embryo snail2, snail1 and twist1 RNAs. Bars indicate percentage loss of expression; the number of embryos is indicated above each bar. (N) The DLMZ of C2/C3 MO-injected embryos was dissected at stage 10.5 and subject to qPCR analysis. The effects on the mesodermal markers xbra, eomes, tbx6, myf5, as well as on wnt8 and fgf8 RNA levels were analyzed. The results shown are representative of studies carried out in triplicate. Error bars indicate s.d.