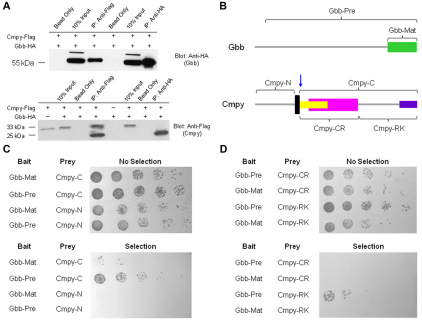
Fig. 7.
Cmpy physically interacts with the Gbb precursor protein. (A) Immunoprecipitation from Drosophila S2R+ cell lysates demonstrates that C-terminal tagged Cmpy-Flag and Gbb-HA fusion proteins form a complex. (Top) Both anti-Flag (Cmpy) and anti-HA (Gbb) precipitate full-length, unprocessed Gbb (55 kDa). (Bottom) Anti-Flag antibody (Cmpy) precipitates both full-length Cmpy (33 kDa) and a processed, smaller Cmpy form (25 kDa). Anti-HA (Gbb) precipitates only the smaller Cmpy isoform. (B) Domains of Cmpy and Gbb used to analyze interaction by yeast two-hybrid. Gbb-Pre is the precursor form of Gbb, including the prodomain and the mature ligand Gbb-Mat. Cmpy-N is the region of Cmpy N-terminal to the transmembrane domain (black), and Cmpy-C is the region of Cmpy C-terminal to the transmembrane domain, including most of the CRR (yellow), the IGFBP domain (magenta) and the arginine/lysine-rich region (purple). The blue arrow indicates the approximate location of the proposed proteolytic processing of Cmpy as indicated by the molecular weight of the smaller Cmpy isoform in A. (C) Yeast two-hybrid interactions demonstrate a physical interaction between Cmpy and Gbb. Gbb-Mat and Gbb-Pre are fused to the GAL4 DNA-binding domain (bait), whereas Cmpy-N and Cmpy-C are fused to the GAL4 activation domain (prey). Cmpy-C interacts strongly with Gbb-Pre and weakly with Gbb-Mat. Cmpy-N does not interact with either region of Gbb in this assay. (D) Yeast two-hybrid analysis demonstrates that the C-terminal portion of Cmpy containing the arginine/lysine-rich region (Cmpy-RK), but not the CRR region (Cmpy-CR), interacts with Gbb-Pre.