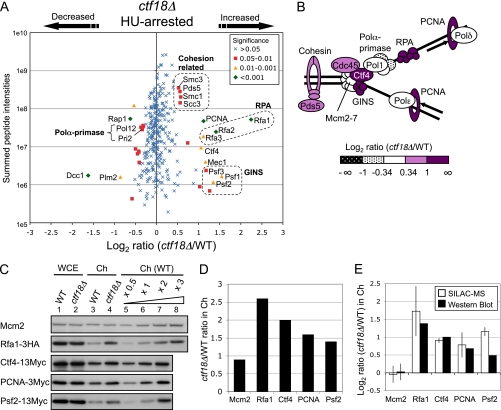
Fig. 3.
Increased chromatin binding of DNA replication proteins, the checkpoint kinase Mec1, and cohesin proteins in HU-treated ctf18Δ cells. A, Plot shows log2 ratios of all chromosome proteins identified and their summed peptide intensities. In this and subsequent plots, the marker symbols indicate significance scores for the changes observed, with green diamonds indicating the highly significant abnormalities and blue crosses changes less likely to be significant. ctf18Δ cells were labeled with [13C6]-Lys. Strains used are SHY201 and TKY1. B, Schematic representation of replisome proteins, colored according to their altered chromatin loading. C, Western blot analysis confirms changed chromatin binding levels. Western blots show whole cell extract (WCE; lanes 1 and 2) and chromatin-enriched (Ch; lanes 3 and 4) fractions from strains with epitope-tagged proteins Rfa1–3HA, Ctf4–13Myc, PCNA-3Myc, or Psf2–13Myc. Loading of Ch fractions was adjusted to be appropriate for each protein analyzed. A dilution series of wild-type chromatin (lanes 5–8) allows the assembly of a standard plot for quantification. Strains used are TKY27, TKY33, TKY25, TKY31, Y1109, SHY164, TKY22, and TKY23. Top panel (Mcm2) shows TKY27 and TKY33. D, Histogram shows ctf18Δ/WT ratios in Ch fraction for each protein, as measured by Western blots. Ratios were calculated based on signal intensities normalized against levels of histone H3 (see also Supplemental Fig. S3). E, Histogram shows ctf18Δ/WT ratios in Ch fraction on log scale, as measured in SILAC analysis (open bars) and by Western blotting (filled bars). For Western blot analysis ratios, mean value and standard deviation (error bar) of Mcm2 from four experiments is shown. For the SILAC analysis ratios, mean values and standard deviations (error bars) are derived from two independent experiments.