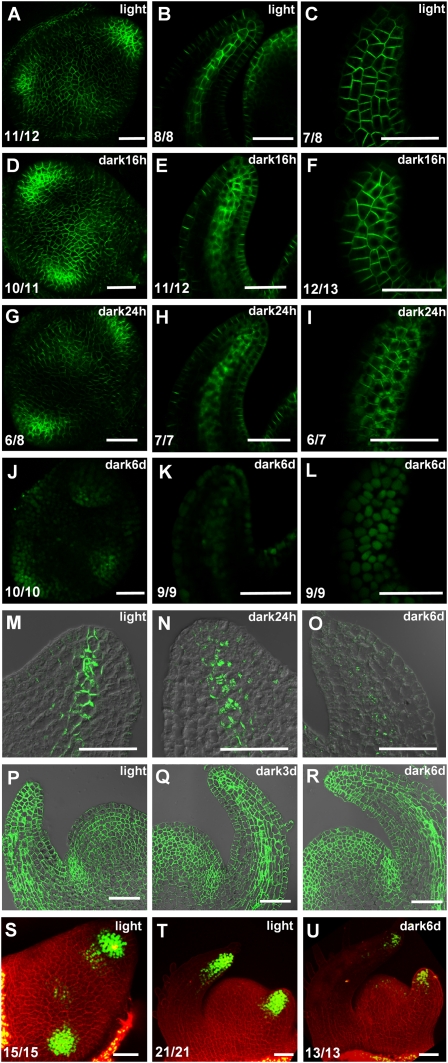
Figure 2.
Darkness affects expression and localization of PIN1 and DR5-YFP. Light-grown tomato PIN1-GFP seedlings (A–C) were transferred to dark for 16 h (D–F), 24 h (G–I), and 6 d (J–L). Maximal projections of transversal confocal sections (A,D,G,J), median longitudinal section of leaf primordia (B,E,H,K), and surface view of leaf epidermis (C,F,I,L). Immunolocalization of PIN1 protein in median longitudinal section of leaf primordia in light-grown plants (M), 24-h dark treated plants (N), or 6-d dark-treated plants (O). Immunolocalization of H+-ATPase in median longitudinal section of shoot apical meristem in light (P), 3-d dark-treated (Q), and 6-d dark-treated (R) plants. (S–U) DR5-YFP expression in tomato shoot apices. Light-grown seedlings (S,T) were transferred to dark for 6 d (U). Maximal projections of transversal confocal sections of the top view (S) and side view (T,U) of a shoot apical meristem. The green signal is AtPIN1-GFP protein in A–L, PIN1 protein in M–O, H+-ATPase protein in P–R, and DR5-YFP protein in S–U. Red signal is propidium-iodide (PI)-stained cell wall. The numbers in the bottom left corner show the number of apices that display the shown expression pattern out of the total number of samples. Bars, 50 μm.