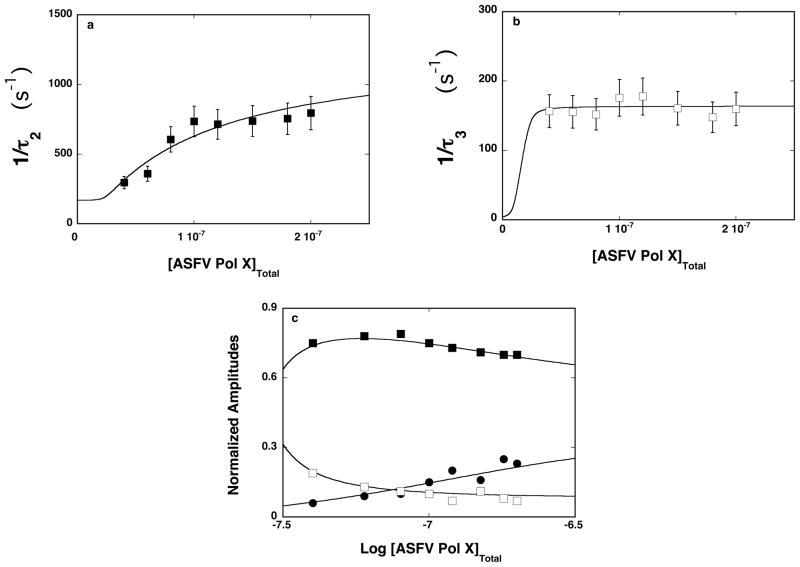
Figure 6.
a. The dependence of the reciprocal of the relaxation time, 1/τ2, for the binding of the ssDNA 20-mer, 5′Fl-dT(pT)-CP-3′, to the total DNA-binding site of the ASFV pol X in buffer C (pH 7.0, 10°C) upon the total concentration of enzyme. The solid line is the nonlinear least-squares fit according to the three-step sequential mechanism, defined by eq. 12 (details in text). The error bars are standard deviations obtained from 3 – 4 independent experiments. b. The dependence of the reciprocal of the relaxation time, 1/τ3, for binding of the ssDNA 20-mer, 5′Fl-dT(pT)-CP-3′, to the total DNA-binding site of the ASFV pol X in buffer C (pH 7.0, 10°C), upon the total concentration of enzyme. The solid line is the nonlinear least-squares fit according to the three-step sequential mechanism, defined by eq. 12. The error bars are standard deviations obtained from 3 – 4 independent experiments. c. The dependence of the normalized, individual relaxation amplitudes of the corresponding relaxation processes, A1, A2, and A3, upon the logarithm of the total concentration of the polymerase. The solid lines are nonlinear least-squares fits according to the three-step sequential mechanism, defined by eq. 12; A1 (●), A2 (■), A3 (❑) (details in text).