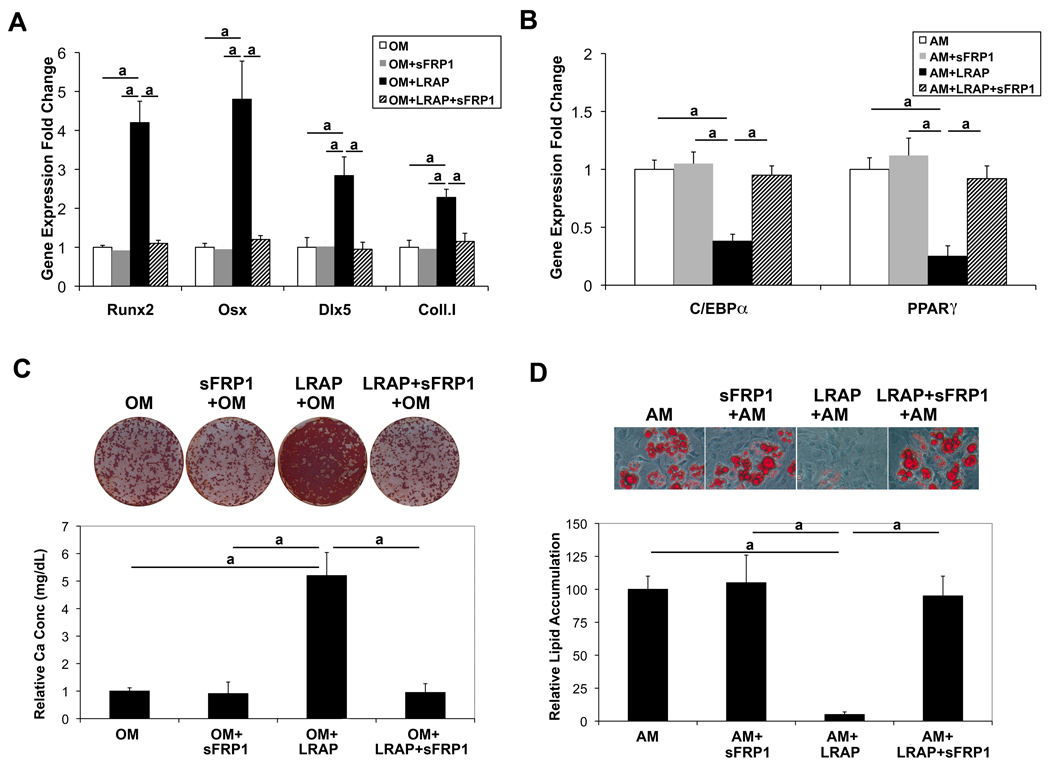
Figure 4. Wnt antagonist sFRP-1 abolishes the effect of LRAP on the stimulation of osteogenesis and the inhibition of adipogenesis of ST2 cells.
ST2 cells were treated with recombinant sFRP-1 (20 ng/ml), along with LRAP (10 ng/ml), and induced to osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation, respectively. LRAP and/or sFRP-1 were maintained in the culture media throughout differentiation as indicated. (A) Two days after osteo-induction, RNA was isolated for quantitative Real-time RT-PCR analysis of osteoblast marker genes: Runx2, Osx, Dlx5 and type I collagen (coll. I). “OM”: osteo-induction in the absence of LRAP; “OM+sFRP-1”: osteo-induction in the presence of sFRP-1; “OM+LRAP”: osteo-induction in the presence of LRAP; “OM+LRAP+sFRP-1”: osteo-induction in the presence of LRAP and sFRP-1. (B) Two days after adipo-induction, RNA was isolated for quantitative Real-time RT-PCR analysis of adipocyte marker genes: C/EBPα and PPARγ “AM”: adipo-induction in the absence of LRAP; “AM+sFRP-1”: adipo-induction in the presence of sFRP-1; “AM+LRAP”: adipo-induction in the presence of LRAP; “AM+LRAP+sFRP-1”: adipo-induction in the presence of LRAP and sFRP-1. (C) Alizarin Red staining for analysis of mineral deposition 2 weeks after osteo-induction. (D) Oil Red O staining for analysis of triglyceride and lipid deposition 8 days after adipo-induction. The graphs represent mean±SD (a: P<0.01).