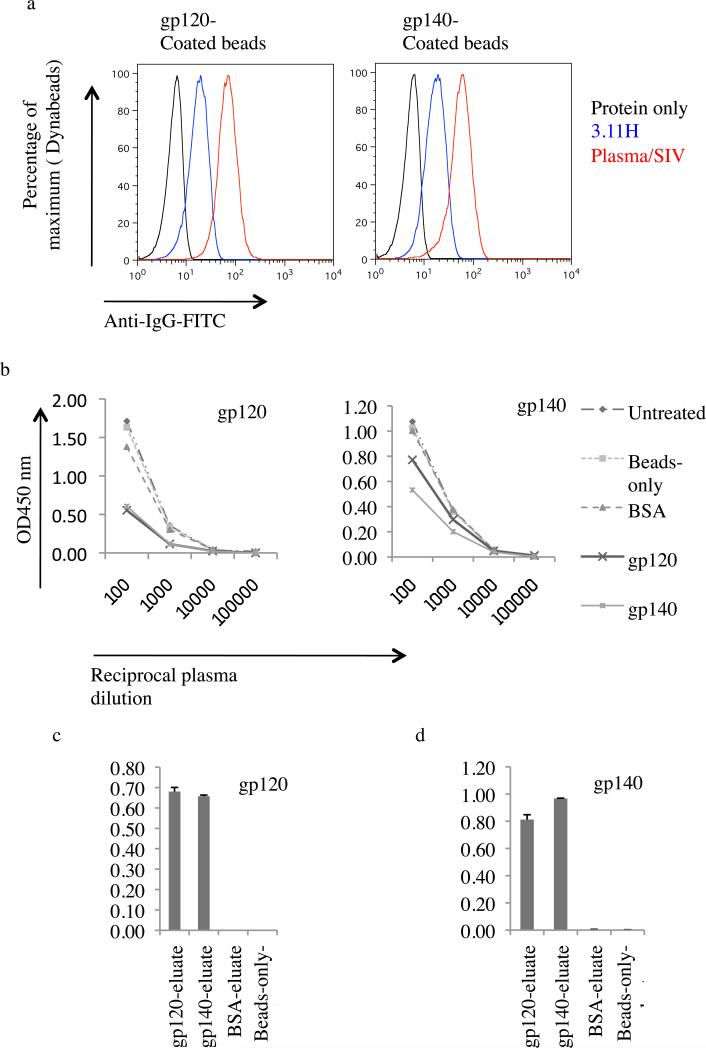
Fig. 4. Plasma antibody adsorption and elution.
(a) Recognition of gp120 and gp140 coated Dynabeads. Coated beads were stained with monoclonal antibody (MAb) 3.11H (V3 loop-specific) and pooled plasmas from SIV-infected monkey (Plasma/SIV+) or buffer only. Antibody binding to gp120 and gp140 was revealed by flow cytometry using an anti-human FITC-conjugated IgG. (b) Anti-gp120 and anti-gp140 antibody adsorption from plasma from SIVmac239Δnef-immunized macaque (Mm 376-04). Antibodies were adsorbed with gp120-coated beads, gp140-coated beads, BSA-coated beads or beads-only or left untreated. Resulting plasmas were then assayed by ELISA for binding to gp120 (left panel) or gp140 (right panel). (c) and (d) Bead-eluate content in anti-SIV ENV-directed antibodies. gp120 and gp140 binding IgGs were eluted with glycine. Eluates were then brought to neutral with Tris-HCl and tested using ELISA plates coated with gp120 and gp140. OD, optical density.