Fig. 2.
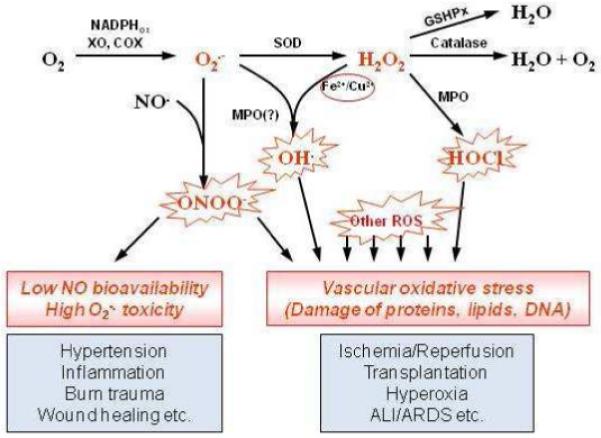
Reactive oxygen species pathways, antioxidant enzymes and their role in vascular oxidative stress. Superoxide is produced by several cellular enzyme systems including NADPH-oxidases, xanthine oxidase, etc. It can react with NO producing aggressive peroxynitrite anion ONOO− and decreasing NO pool. Superoxide spontaneously or by action of superoxide dismutase may be reduced into hydrogen peroxide H2O2. Hydrogen peroxide can produce extremely reactive hydrogen radical ·OH in the presence of transition metals or hypochlorous acid by myeloperoxidase. Catalase and glutathione peroxidases protect cells against hydrogen peroxide. ALI/ARDS, acute lung injury/acute respiratory distress syndrome; COX, cyclooxygenase; GSHPx, glutathione peroxidases; MPO, myeloperoxidase; ROS, reactive oxygen species; SOD, superoxide dismutase; XO, xanthine oxidase.
