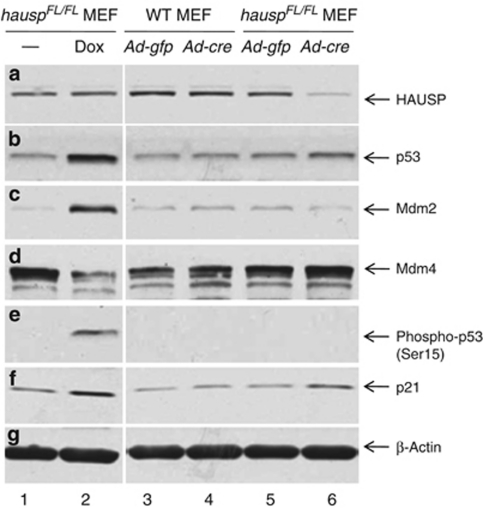
Figure 6.
Deletion of hausp in MEFs resulted in destabilization of Mdm2 and stabilization of p53. Protein extracts were prepared from hauspFL/FL MEFs infected with control virus (Ad-CMV-GFP; lane 5) and Cre-expressing adenovirus (Ad-CMV-Cre; lane 6), as well as from wild-type MEFs infected with control virus (lane 3) and Cre-expressing adenovirus (lane 4). Protein extracts were also prepared from hauspFL/FL MEFs treated without (lane 1) and with doxorubicin (lane 2) for 6 h to induce DNA damage response. The protein levels of HAUSP (a), total p53 (CM5) (b), Mdm2 (c), Mdm4 (d), Phospho-p53 (Ser15) (e), p21 (f), and protein loading control β-actin (g) were determined by western blot. Deletion of hausp resulted in depletion of HAUSP (a; lane 6 versus 5), accumulation of p53 (b; lane 6 versus 5), destabilization of Mdm2 (c; lane 6 versus 5), and activation of p21 (f; lane 6 versus 5). There was slight increase of Mdm4 level in hausp knockout MEFs (d; lane 6 versus 5). No change in phosphorylation on Ser15 of p53 was observed in hausp knockout cells (e; lane 6 versus 5). In contrast, DNA damage caused activation of p53 (b; lane 2 versus 1), increase of Mdm2 (c; lane 2 versus 1), decrease of Mdm4 (d; lane 2 versus 1), phosphorylation on Ser15 of p53 (e; lane 2 versus 1), and activation of p21 (f; lane 2 versus 1). There was no obvious change of protein levels for Hausp, p53, Mdm2, Mdm4, and p21 in wild-type MEFs infected with either control adenovirus or Cre-expressing adenovirus (lanes 3 and 4). The protein levels of β-actin indicated comparable levels of total proteins in each lane (g)