Figure 6.
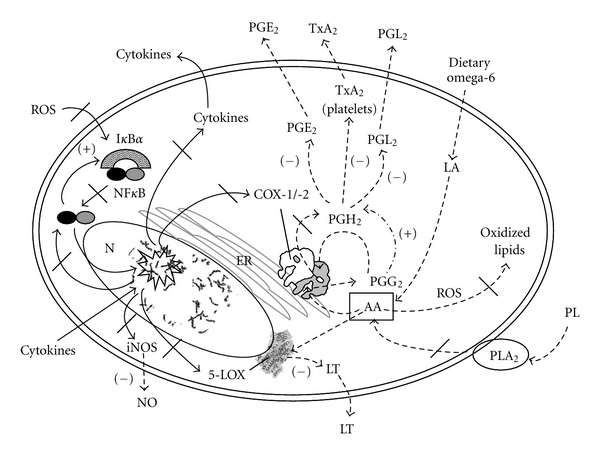
Flavocoxid's putative mechanism of action inhibiting nuclear (N) ROS activation (black slash) of NFκB which induces gene expression (star burst) of cox-2, 5-lox, cytokines, and inos (black slash) through a strong antioxidant stimulatory activity. Dietary omega-6 fatty acids are converted to linoleic acid (LA) (dotted line) and then to AA which are processed through the COX and 5-LOX enzymes. Flavocoxid works on the protein level to limit the production of AA from phospholipids (PL) by inhibiting PLA2. It also has been shown to modulate (−) PGE2, PGI2, and TxA2 generation (dotted line) via an anti-PO activity of endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-anchored COX-1 and COX-2 as well as inhibition of nucleus (N)-associated 5-LOX to decreased LTB4 production (−). PGH2 may be produced (+) from PGG2 through and alternate peroxidase activity (dash and dotted line). Flavocoxid has also been shown to restore IκBα regulation of NFκB (+).
