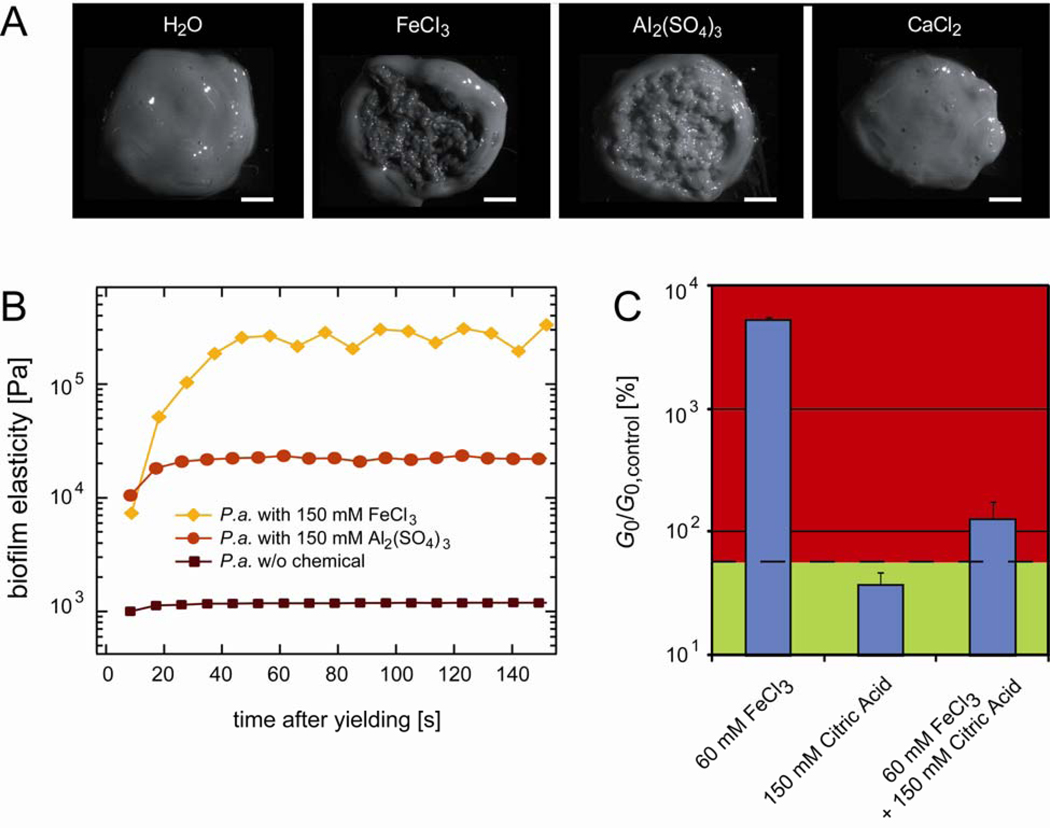
Figure 3.
Response of Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms to trivalent ions. (A) Texture of collected P.a. biofilms after a drop of a chemical solution is added to the center of the biofilm and distributed by gentle stirring. 250 mM Ca2+ ions do not alter the biofilm texture compared to the control, whereas 150 mM Fe(III) and 150 mM Al3+ evoke a granular, sand-like texture. The scale bars denote 2 mm. (B) The speed of the mechanical recovery process of P.a. biofilms depends on the biofilm elasticity. PAO1 biofilms without any chemical additions fully recover within ~20 s after yielding. This recovery time increases up to ~1min if the biofilm is treated with 150 mM Al3+ or Fe(III), respectively. (C) Fe(III) and citric acid act antagonistically and inhibit each other. For all data shown, 5% (v/w) of an aqueous solution containing different amounts of chemicals were added to the biofilm material. The dashed base line indicates the elasticity of a P.a. biofilm modified with 5% (v/w) water only.