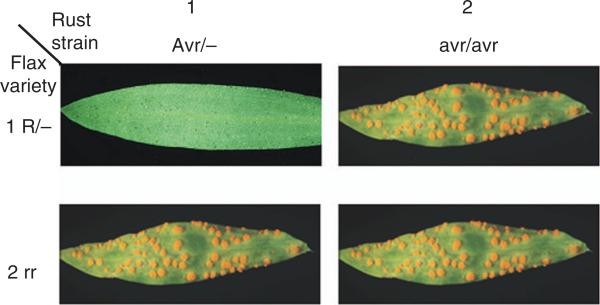
Fig. 1.
Gene-for-gene resistance. Quadratic diagram illustrating the gene-for-gene interaction between host resistance (R) genes and rust avirulence (Avr) genes. Resistance occurs when a rust (strain 1) carrying a dominant Avr gene allele attempts to infect a host plant (variety 1) carrying the corresponding dominant R gene allele. If the rust (strain 2) lacks the Avr allele, that is, it is homozygous for the virulence allele (avr), then it is not recognised by the plant and can cause disease. Likewise, if the plant (variety 2) lacks the R gene; that is, it is homozygous for the recessive susceptibility allele (r), then it is does not recognise the rust and is susceptible to infection.