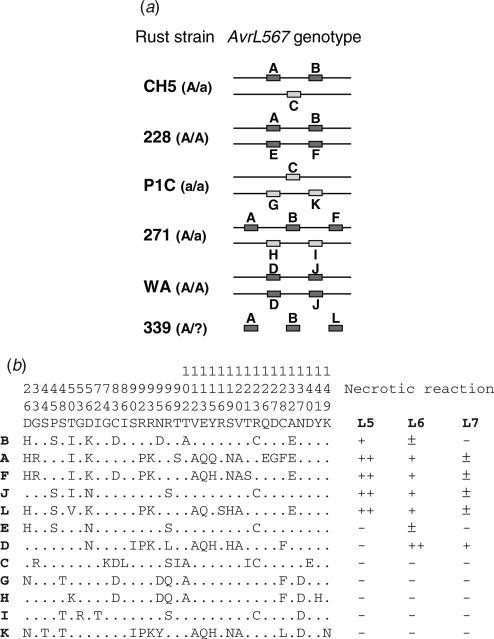
Fig. 3.
The AvrL567 locus is highly polymorphic. (a) The AvrL567 gene variants (A–L) present at each allele in various rust strains which are either homozygous (A/A) or heterozygous (A/a) for avirulence or are virulent (aa) on L5, L6 and L7. AvrL567 gene variants with a positive avirulence function are darkly shaded, while genes with no detected function are lightly shaded. Rust CH5 is the result of a cross between rusts 228 and P1C. Although rust 339 is avirulent, its genotype is not known. Rust strain WA was isolated from a native Australian Linum marginale population. (b) The consensus amino acid at each of the polymorphic positions (numbered above the consensus line) in the AvrL567 homologues is shown above the individual sequences with identical residues indicated by dots. The final columns indicate whether a necrotic response (+) was observed when these proteins were expressed in flax lines containing L5, L6 or L7. ++ indicates a very strong necrotic response, while [notdef] indicates a weak response.