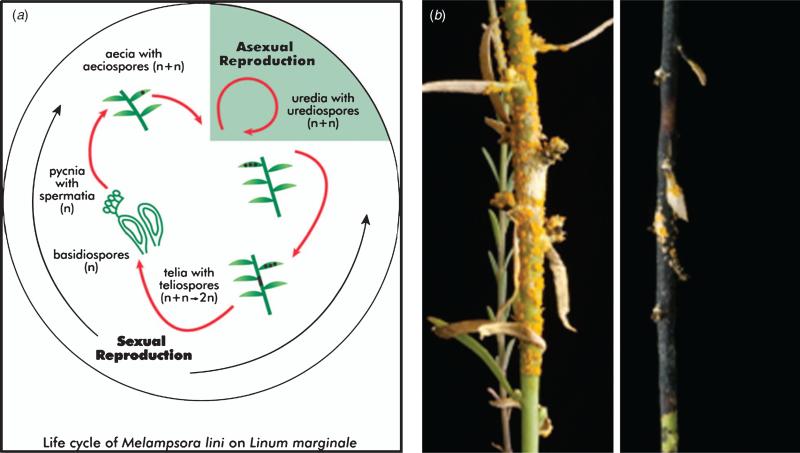
Fig. 5.
Life cycle of Melampsora lini. (a) Schematic diagram illustrating the lifecycle of Melampsora lini. During the growing season, dikaryotic rust urediospores infect flax plants and reproduce asexually (shaded portion of the diagram). Multiple asexual cycles can occur during a single growing season. Under some environmental conditions the sexual cycle can be induced late in the season leading to production of diploid teliospores that are resistant to environmentalextremes.Teliosporegerminationinducesmeiosisgivingriseto haploidbasidiospores.Basidiosporeinfectionleads toformationofpycnia, and mating requires transfer of haploid pycniospores between pycnia. This induces production of the aeciospores which then initiate the dikaryotic infection stage. (b) M. lini infection of Linum marginale. Left panel shows the asexual uredinial stage infection, while the right panel shows telia formation which intiatites the sexual cycle.