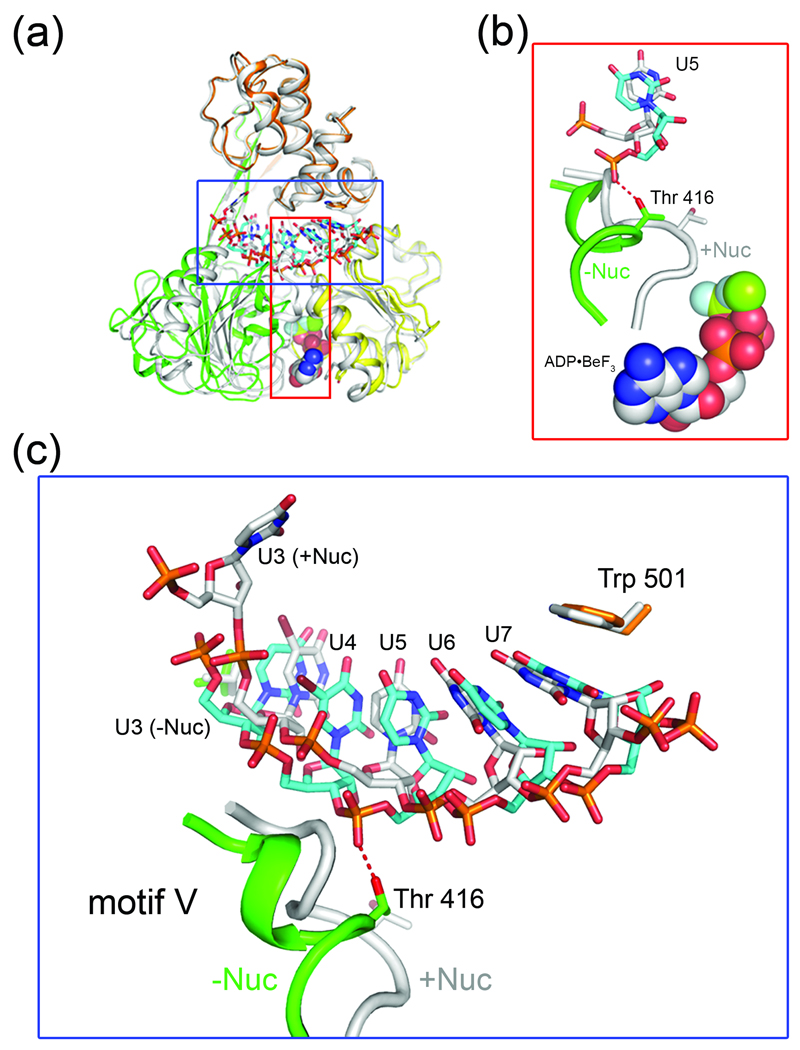
Fig. 5.
Nucleotide induced conformational changes in NS3 lead to differences in RNA binding. (a) Structural overlay of nucleotide-free NS3-rU8Br4 (colored according to Fig. 1) and NS3-rU8Br4/ADP•BeF3 (gray). (b) Local conformational change in of motif V of D2. Motif V (residues 411–419) in the nucleotide-free structure (green helical coil and sticks) rearranges upon binding to ADP•BeF3 (spheres), resulting in the repositioning of Thr 416. For clarity, only U5 of the RNA is shown (cyan sticks, nucleotide-free structure; gray sticks, nucleotide-bound structure). (c) Comparison of RNA binding to NS3 in the nucleotide-bound and nucleotide-free states. The nucleotide-bound structure (+Nuc, gray coil and sticks) and the nucleotide-free structure (−Nuc, green coils and cyan sticks) are overlaid. Thr 416, Trp 501 and RNA nucleotides are labeled accordingly.