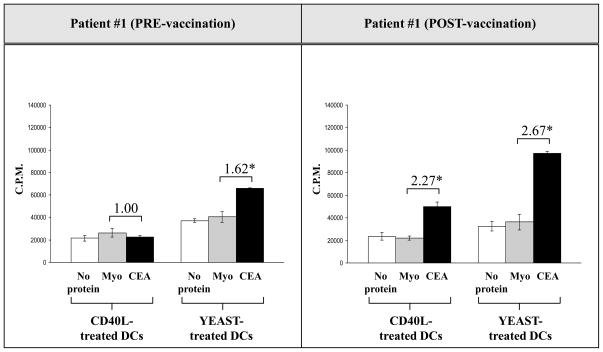
Fig. 3.
CEA-specific CD4+ T-cell proliferation increased in a colorectal cancer patient pre- and post-vaccination when CD4+ T cells were stimulated with DCs treated with yeast and incubated with CEA protein. DCs from a colorectal cancer patient were isolated pre- and post-vaccination and cultured for 5 days with GM-CSF and IL-4. DCs were then treated with yeast (yeast:DCs = 10:1) for 48 h or with CD40L (1 μg/ml) for 24 h. CD4+ T cells were isolated using Miltenyi columns by negative selection and incubated with DCs (CD4+ T cells:DCs = 10:1) for 7 days, using 2 μg/ml PHA as a positive control and 20 μg/ml myoglobulin as a negative control. CEA protein was used at 20 μg/ml. On day 7, 3H was added to the culture, incubated for 6 h, and read with a Wallac Trilux B-scintillation counter. The numbers above the CEA columns represent the fold increase of CD4 proliferation with CEA protein and myoglobulin protein. The experiment was performed in triplicate and the results are expressed as the mean ± SD (cpm).