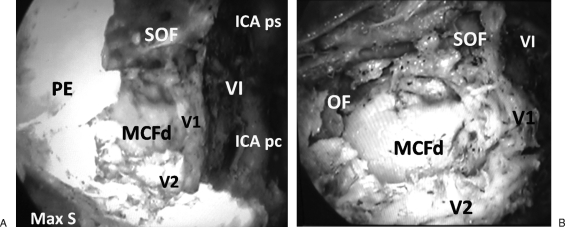
Figure 3.
(A) Endoscopic view showing right cavernous sinus apex. The bone trajectory between V2 canal and superior orbital fissure (SOF) is drilled in addition to bone of middle cranial fossa (MCF) inferomedial to ophthalmic nerve (V1). The posterior ethmoid (PE) and maxillary sinus (Max S) limit the approach laterally. Medially, the abducent nerve (VI) appears as the most superficial nerve in the medial wall of cavernous sinus. The parasellar (ICA ps) and paraclival (ICA pc) segments of cavernous internal carotid artery limit the approach medially. (B) Endoscopic view showing the orbital floor (OF) slopes toward anterior end of V2 canal at PPF. The MCF dura (MCF d) appears between V1 and V2. Abducent nerve (VI) appears lateral and superior to V1, which branches before entering SOF.