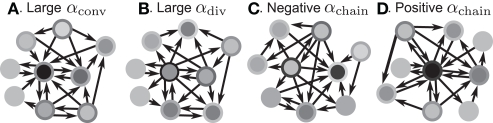
Figure 3.
Illustrations of networks with different connectivity statistics. All networks contain N = 9 neurons with Nconn = 22 connections, so that the connection probability is . For each neuron, darker inner color indicates larger in-degree and darker outer color indicates larger out-degree. (A) Network with large convergence. There is large variance in in-degree. Nrecip = 4, Nconv = 42, Ndiv = 23, and Nchain = 45 so that , , , and . (B) Network with large divergence (the same network as in panel A, but with connections reversed). There is large variance in out-degree. Nrecip = 4, Nconv = 23, Ndiv = 42, and Nchain = 45 so that , , , and . (C) Network with few chains. Neurons with large in-degree tend to have small out-degree, and neurons with large out-degree tend to have small in-degree. Nrecip = 2, Nconv = 33, Ndiv = 35, and Nchain = 29 so that , , , and . (D) Network with many chains. Neurons with large in-degree tend to have large out-degree. Nrecip = 6, Nconv = 33, Ndiv = 33, and Nchain = 65 so that , , , and .