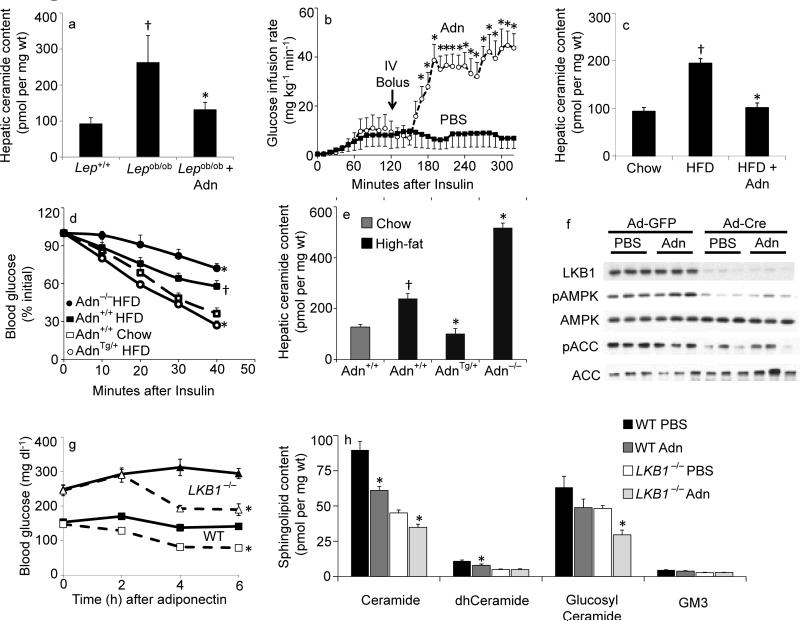
Fig 1. Adiponectin rapidly lowers hepatic ceramide content and improves glucose homeostasis.
(a) Total ceramide levels were quantified from liver of leptin deficient (ob/ob) mice after 60-minute treatments with full length adiponectin (Adn, 2 mg/kg, IV) or PBS (n=6/group). (b) Glucose infusion rates were calculated during hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamps peformed on conscious unrestrained ob/ob mice before and after a bolus of adiponectin (Adn, 2 mg/kg, IV) or PBS (n=5/group). (c) Total ceramide levels were quantified from liver of diet induced obese mice after 60-minute treatments with full length adiponectin (Adn, 2 mg/kg, IV) or PBS (n=9/group). (d–e) Adiponectin deficient (−/−), wildtype (+/+), or overexpressing mice (+/Tg) were maintained on high-fat diets (solid lines) or normal chow (dashed line) for 8 weeks prior to determination of (d) insulin tolerance and (e) hepatic ceramide content (n=7/group). (f–h) LKB1(fl/fl) mice were infected with adenovirus encoding either GFP or Cre recombinase 16 days prior to experiments (n=8/group). (f) Western blots of liver proteins probing against LKB1, phospho(T172)-AMPK, AMPK, phosphor(S79)-ACC1, and ACC1 (displayed in triplicate). (g) Whole blood glucose was monitored for 6 hours following injection of PBS (solid lines) or adiponectin (34 mg/kg, IV, dashed line). (h) Total hepatic sphingolipid levels were quantified by tandem MS/MS. * denotes significant effect of adiponectin (p<0.01). † Denotes significant effect of as compared to lean wildtype controls (p<0.05).