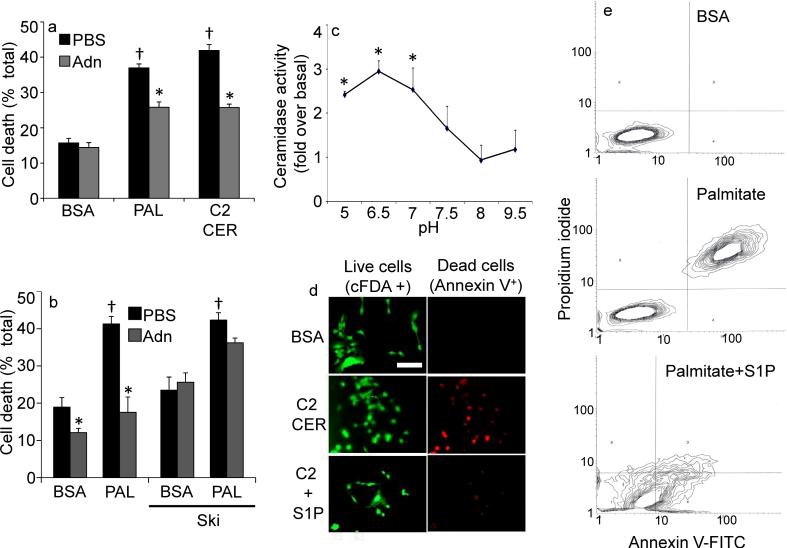
Fig 4. Adiponectin alters sensitivity to ceramide-induced apoptosis in INS-1 β-cells.
(a) INS-1 cells were washed and removed to 2% BSA, Palmitate (750 μM in 2% BSA), or C2-Ceramide (50 μM in 2% BSA). Adiponectin (3 μg/mL) or PBS was immediately added and cell viability was determined after 18 hours (n=6/group from 3 separate experiments). (b) Cell viability was determined on INS-1 cells pretreated with sphingosine kinase inhibitor (2-(p-Hydroxyanilino)-4-(p-chlorophenyl) thiazole, 0.5 μM) or DMSO prior to delivery of adiponectin (3μg/mL) or PBS and maintained for 18 hours in the presence of 2% BSA or Palmitate (750 μM in 2% BSA) (c) Ceramidase activity was determined in lysates from cultured INS-1 cells under a range of pH conditions (n=4 from separate experiments) in the presence or absence of adiponectin (0.3 μg/mL, in vitro). “Fold change over baseline” refers to the change compared to BSA treatment without adiponectin. (d) INS-1 cells were challenged with C2-ceramide (50 μM) in the presence or absence of S1P (5 μM) cell death was determined by live/dead staining with cFDA or annexin V (image is representative of 3 separate experiments, bar=50μm). (e) Apoptosis of INS-1 cells was determined by FACS analysis of annexin V and propidium iodide stained cells following 18 hours of treatment with BSA, palmitate (750 μM), or coadministered palmitate and S1P (5μM) (representative of 3 independent experiments). * denotes significant (p<0.01) effect of adiponectin. † denotes significant (p<0.01) effect of pro-apoptotic insult.