Abstract
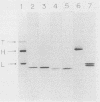
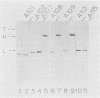
After treatment of Clostridium botulinum type A neurotoxin with papain, three fragments (Mrs, 101,000, 45,000, and 43,000) were purified by hydrophobic and ion-exchange chromatography with a high-performance liquid chromatographic system. Immunoblotting analyses with monoclonal antibodies showed that the 101,000-dalton fragment consisted of the light chain and a part of the heavy chain (H-1 fragment) linked together by a disulfide bond, and the other two fragments were correlated to the remaining portion of the heavy chain (H-2 fragment). The 45,000- and 43,000-dalton fragments effectively competed for binding of the 125I-labeled neurotoxin to synaptosomes, while no inhibition was observed with the 101,000-dalton fragment. The results indicate that the H-2 fragment interacts with the binding site on the neural membrane. The binding of the neurotoxin was impaired by treatment of synaptosomes with neuraminidase. Incorporation of gangliosides into neuraminidase-treated synaptosomes resulted in the restoration of binding. The results suggest that gangliosides are one of the components of the toxin-binding site.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMINOFF D. The determination of free sialic acid in the presence of the bound compound. Virology. 1959 Mar;7(3):355–357. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(59)90207-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bandyopadhyay S., Clark A. W., DasGupta B. R., Sathyamoorthy V. Role of the heavy and light chains of botulinum neurotoxin in neuromuscular paralysis. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 25;262(6):2660–2663. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bigalke H., Müller H., Dreyer F. Botulinum A neurotoxin unlike tetanus toxin acts via a neuraminidase sensitive structure. Toxicon. 1986;24(11-12):1065–1074. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(86)90133-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black J. D., Dolly J. O. Interaction of 125I-labeled botulinum neurotoxins with nerve terminals. I. Ultrastructural autoradiographic localization and quantitation of distinct membrane acceptors for types A and B on motor nerves. J Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;103(2):521–534. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.2.521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DasGupta B. R., Sugiyama H. A common subunit structure in Clostridium botulinum type A, B and E toxins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Jul 11;48(1):108–112. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90350-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. M., Williams R. S., Shone C. C., Hambleton P., Melling J., Dolly J. O. Botulinum neurotoxin type B. Its purification, radioiodination and interaction with rat-brain synaptosomal membranes. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Jan 15;154(2):409–416. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09413.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habermann E., Dreyer F. Clostridial neurotoxins: handling and action at the cellular and molecular level. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1986;129:93–179. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-71399-6_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helting T. B., Zwisler O. Structure of tetanus toxin. I. Breakdown of the toxin molecule and discrimination between polypeptide fragments. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jan 10;252(1):187–193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwamori M., Nagai Y. A new chromatographic approach to the resolution of individual gangliosides. Ganglioside mapping. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Feb 27;528(2):257–267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura M., Iwamori M., Nagai Y. Interaction between Clostridium botulinum neurotoxin and gangliosides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Mar 20;628(3):328–335. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(80)90382-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura M., Sone S. Binding ability of Clostridium botulinum neurotoxin to the synaptosome upon treatment of various kinds of the enzymes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Mar 30;143(3):928–933. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90339-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo H., Shimizu T., Kubonoya M., Izumi N., Takahashi M., Sakaguchi G. Titration of botulinum toxins for lethal toxicity by intravenous injection into mice. Jpn J Med Sci Biol. 1984 Jun;37(3):131–135. doi: 10.7883/yoken1952.37.131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozaki S. Interaction of botulinum type A, B and E derivative toxins with synaptosomes of rat brain. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1979 Jul;308(1):67–70. doi: 10.1007/BF00499721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozaki S., Kamata Y., Nagai T., Ogasawara J., Sakaguchi G. The use of monoclonal antibodies to analyze the structure of Clostridium botulinum type E derivative toxin. Infect Immun. 1986 Jun;52(3):786–791. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.3.786-791.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozaki S., Ogasawara J., Shimote Y., Kamata Y., Sakaguchi G. Antigenic structure of Clostridium botulinum type B neurotoxin and its interaction with gangliosides, cerebroside, and free fatty acids. Infect Immun. 1987 Dec;55(12):3051–3056. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.12.3051-3056.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozaki S., Togashi S., Sakaguchi G. Separation of Clostridium botulinum type A derivative toxin into two fragments. Jpn J Med Sci Biol. 1981 Apr;34(2):61–68. doi: 10.7883/yoken1952.34.61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maisey E. A., Wadsworth J. D., Poulain B., Shone C. C., Melling J., Gibbs P., Tauc L., Dolly J. O. Involvement of the constituent chains of botulinum neurotoxins A and B in the blockade of neurotransmitter release. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Nov 15;177(3):683–691. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14423.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakaguchi G. Clostridium botulinum toxins. Pharmacol Ther. 1982;19(2):165–194. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(82)90061-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shone C. C., Hambleton P., Melling J. Inactivation of Clostridium botulinum type A neurotoxin by trypsin and purification of two tryptic fragments. Proteolytic action near the COOH-terminus of the heavy subunit destroys toxin-binding activity. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Aug 15;151(1):75–82. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09070.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson L. L. Molecular pharmacology of botulinum toxin and tetanus toxin. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1986;26:427–453. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.26.040186.002235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugii S., Sakaguchi G. Molecular construction of Clostridium botulinum type A toxins. Infect Immun. 1975 Dec;12(6):1262–1270. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.6.1262-1270.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiyama H. Clostridium botulinum neurotoxin. Microbiol Rev. 1980 Sep;44(3):419–448. doi: 10.1128/mr.44.3.419-448.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takamizawa K., Iwamori M., Kozaki S., Sakaguchi G., Tanaka R., Takayama H., Nagai Y. TLC immunostaining characterization of Clostridium botulinum type A neurotoxin binding to gangliosides and free fatty acids. FEBS Lett. 1986 Jun 9;201(2):229–232. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80614-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITTAKER V. P. The isolation and characterization of acetylcholine-containing particles from brain. Biochem J. 1959 Aug;72:694–706. doi: 10.1042/bj0720694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. S., Tse C. K., Dolly J. O., Hambleton P., Melling J. Radioiodination of botulinum neurotoxin type A with retention of biological activity and its binding to brain synaptosomes. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Mar 15;131(2):437–445. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07282.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]