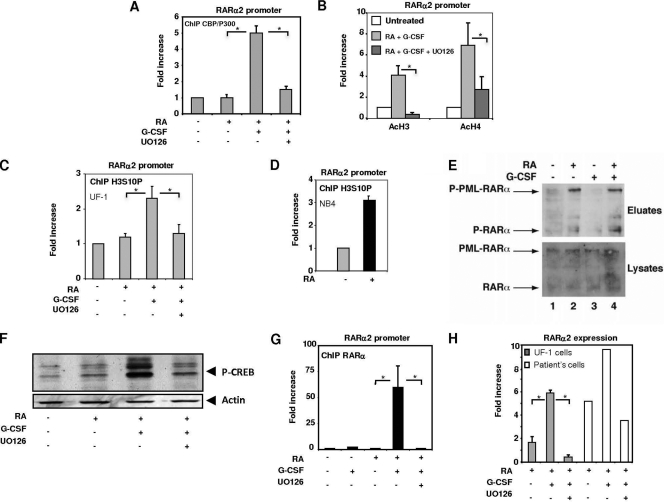
Fig. 6.
G-CSF-activated ERKs restore RA target gene transcription through histone phosphorylation. (A and B) ChIP experiments showing that the MEK inhibitor UO126 reduces the recruitment of CBP/p300 (A) and the acetylation of histones H3 and H4 (B) to the RARα2 promoter, induced by the RA–G-CSF combination. (C and D) ChIP analysis of histone H3 phosphorylation in NB4 and UF-1 cells treated with RA and/or G-CSF. (E) G-CSF does not affect the RA-induced phosphorylation of RARα and PML-RARα in UF-1 cells as assessed by immunoblotting after phosphoprotein affinity purification. (F) G-CSF induces the phosphorylation of CREB through ERKs. (G) ChIP analysis of RARα recruitment to the RARα2 promoter in UF-1 cells treated with the RA–G-CSF combination in the absence or presence of UO126. (H) qRT-PCR analysis of the RARα2 gene expression in UF-1 cells or fresh patient cells treated with the RA–G-CSF combination in the presence or absence of the MEK inhibitor UO126. In all panels, values are the mean ± SD of duplicates performed with at least two separate experiments. * indicates a P value of <0.05 as determined by two-tailed Student's t test.