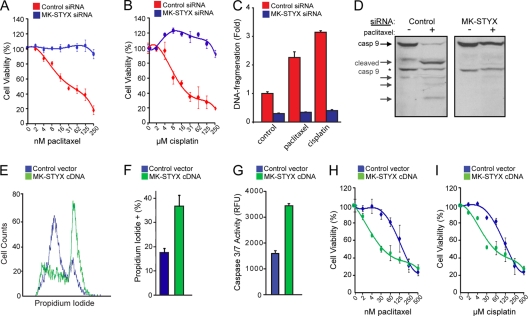
Fig. 2.
MK-STYX expression regulates the cellular response to chemotherapeutics. (A and B) HeLa cells transfected with control or MK-STYX-specific siRNA were treated with a dose response of paclitaxel (A) or cisplatin (B), and cell viability was measured 24 h posttreatment using the cell titer blue assay. The error bars indicate standard deviations. (C) Control or MK-STYX siRNA-transfected HeLa cells were treated with 100 nM paclitaxel or 50 μM cisplatin for 24 h, and apoptosis was assayed by a DNA fragmentation ELISA. (D) Control or MK-STYX siRNA-transfected HeLa cells were treated with 100 nM paclitaxel or 50 μM cisplatin for 24 h, and caspase 9 activation was assayed through the appearance of cleaved isoforms via immunoblotting, indicating the initiation of the intrinsic apoptotic cascade. The asterisk indicates a constitutive form of cleaved caspase 9 found even in healthy cells. (E and F) HeLa cells were transfected with MK-STYX cDNA for 24 h. Cell death was measured by propidium iodide uptake (E) and quantified (F). (G) Introduction of exogenous MK-STYX drives caspase 3/7 activation in HeLa cells. (H and I) Introduction of MK-STYX in 293FT cells increases cell death in the presence of both paclitaxel (H) and cisplatin (I), as measured using the cell titer blue assay.