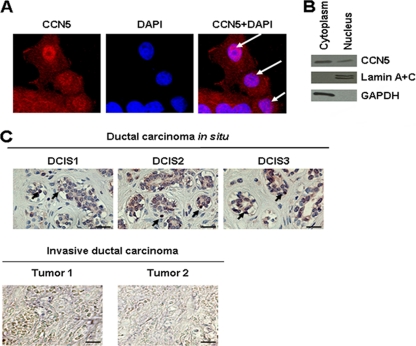
Fig. 1.
Subcellular localization of CCN5. (A) Immunochemical detection. MCF-7 cells were fixed, permeabilized, and then immunostained with anti-CCN5 antibodies as described in Materials and Methods. Nuclear DNA was stained with DAPI. Images were obtained by confocal microscopy (magnification, ×63). The results were confirmed by three independent experiments. Arrows indicate nuclear structure stained with anti-CCN5 antibodies. (B) Biochemical evidence. MCF-7 cells were fractionated into cytosolic and nuclear fractions, and equal amounts of protein were analyzed by Western blotting. GAPDH was used as a cytoplasmic marker, and lamin A and C were used as nuclear markers to exclude cross-contamination. (C) Immunohistochemistry analysis of human DCIS and invasive carcinoma sections using anti-CCN5 antibodies. Arrows indicate marked nuclei. Scale bars, 100 μm.