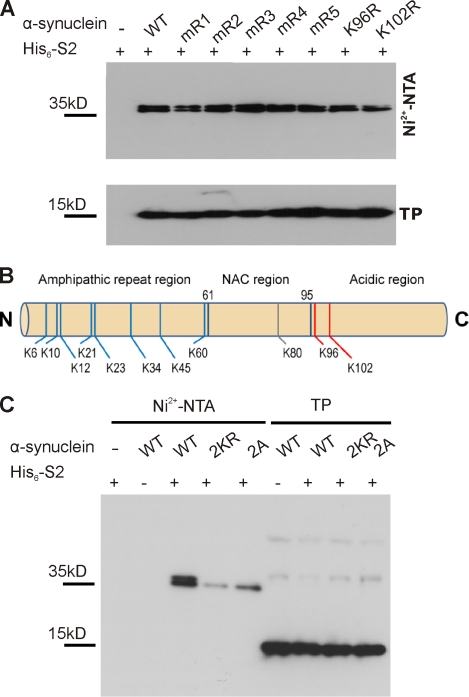
Figure 3.
K96 and K102 are the major sumoylation sites of α-synuclein. (A) α-Synuclein is sumoylated at multiple lysine residues. Sumoylation of α-synuclein was analyzed in HEK293T cells by cotransfection of His6-SUMO2 with WT myc-tagged α-synuclein or one of the indicated lysine-to-arginine mutants (mR1: K6, 10, and 12R; mR2: K21 and 23R; mR3: K32 and 34R; mR4: K43 and 45R; and mR5: K58, 60R, K96R, and K102R), followed by Ni2+-NTA chromatography. None of the mutations resulted in abolished α-synuclein sumoylation. Total protein (TP) levels of WT α-synuclein and the respective mutants are shown in the bottom panel. Samples were analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-myc antibody (9E10). (B) Summary of α-synuclein sumoylation sites. MS analysis of sumoylated α-synuclein (obtained upon sumoylation in bacteria; see Materials and methods) revealed 11 SUMO-conjugated lysine residues (8 lysines in the N-terminal amphipathic region, 1 lysine in the hydrophobic NAC region, and the 2 lysines in the C-terminal acidic region; Fig. S2 and supplemental data). Nonconsensus lysines are depicted in blue, and the consensus and consensus sequence–related sites are in red. (C) The sumoylation levels of myc-tagged WT, 2KR (K96R and K102R), and 2A (D98A and E104A) mutants were compared using Ni2+-NTA chromatography. Elution samples and total lysates (TP) in A and C were run on a 4–12% NuPAGE Bis-Tris gel and analyzed by immunoblotting with myc antibody (clone 9E10). Sumoylated α-synuclein runs as a doublet band on gradient SDS-PAGE.