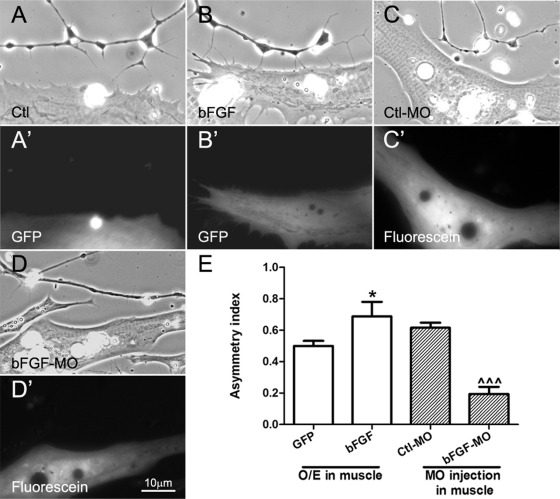
FIGURE 5:
Effects of manipulating muscle bFGF expression on axonal filopodial asymmetry. Spinal neurons were cocultured with muscle cells isolated from embryos expressing GFP (A, A′), GFP plus exogenous bFGF (B, B′), control morpholinos (C, C′), or bFGF morpholinos (D, D′). Overexpression of bFGF in muscle led to enhanced filopodial asymmetry in neurons compared with that in cocultures using control GFP-expressing muscle. On the other hand, muscle cells bearing bFGF but not control morpholinos suppressed axonal filopodial asymmetry. (E) Quantification of these results. Values shown are mean ± SEM; t test, *p < 0.05 for comparisons of neurons near GFP- and GFP/bFGF–expressing muscle cells, and ^^^p < 0.001 for comparison of neurons near Ctl-MO– and bFGF-MO–injected muscle cells.