FIGURE 1:
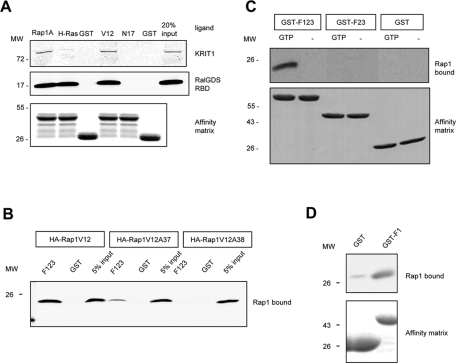
KRIT1 is a Rap1-specific effector protein, and its interaction with Rap1 requires the F1 subregion of the FERM domain and the switch I domain of Rap1. (A) Recombinant bead-bound GST-Rap1A, GST-H-Ras, and GST were used to isolate recombinant KRIT1 and RalGDS from cell lysates. KRIT1 binds to Rap1A but not H-Ras or GST, whereas RalGDS binds to both Rap and Ras proteins (left). KRIT1 preferentially binds active Rap1A (GST-Rap1V12) and does not bind to an inactive Rap1 variant (GST-Rap1N17) or to GST only (right). GST blot is shown as loading control. Blots are representative; n = 3. Blots were cropped, and intervening lanes were removed using Adobe Photoshop. (B) KRIT1–Rap1A interaction involves residues within the switch 1 domain of Rap1A. Recombinant Rap1A (V12) from HEK293 cell lysate binds to GST-F123 (left). Single-alanine mutation on a switch 1 domain residue D38 (Rap1V12A38) does not bind to GST-F123 (right). Another switch 1 domain mutant (Rap1V12A37) dramatically reduces the binding to GST-F123 (middle). Blots are representative of three experiments. (C) KRIT1 binding to Rap1A is GTP dependent. Recombinant Rap1A from cell lysate binds to the KRIT1 FERM domain (GST-F123) only in the presence of GTP (10 mM). Binding of Rap1A to GST-KRIT1 FERM is lost on deletion of the F1 region, as binding to truncated FERM domain protein (GST-F23) is not observed (top). Expression of GST constructs is shown at bottom; blots are representative of three experiments. (D) F1 subregion of KRIT1 FERM domain is sufficient for Rap1A binding. Top, recombinant Rap1A (V12) binds to GST-F1 (right) but not GST alone (left). Bottom, equal loading of both GST fusion proteins as judged by SDS–PAGE and Coomassie Blue staining. Blots are representative of three experiments.