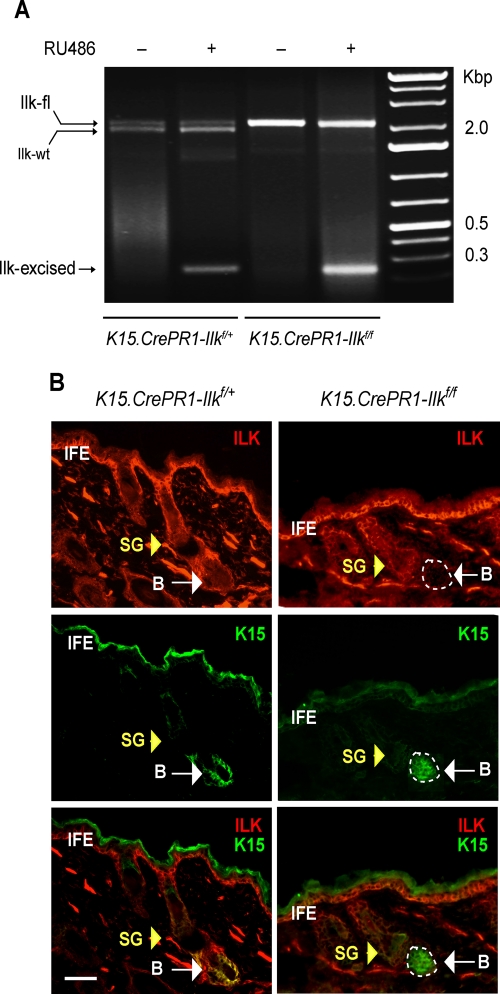
FIGURE 1:
Conditional Ilk gene inactivation in stem cells of the hair follicle bulge. (A) Dorsal skin of P50 K15.CrePR1-Ilkf/+ or K15.CrePR1-Ilkf/f mice was treated daily with topical RU486 (+) or vehicle (–) for 5 d. Genomic DNA from treated skin was isolated and genotyped. Amplicons corresponding to the floxed (2.1 Kb), wild-type (wt, 1.9 Kb), and Cre-excised (230 base pairs) Ilk alleles are indicated. (B) Dorsal skin of P50 K15.CrePR1-Ilkf/+ or K15.CrePR1-Ilkf/f mice was treated daily with topical RU486 for 5 d. The skin was harvested 5 d later, and tissue sections were processesed for immunofluorescence microscopy, using rabbit anti-ILK and mouse anti-K15 antibodies, as indicated. Yellow and white arrows show the sebaceous gland (SG) and the hair follicle bulge (B), respectively. IFE, interfollicular epidermis. The apparent K15 staining in the IFE is due to antibody trapping by keratin filaments overlaying the cornified layer. Bar, 50 μm.