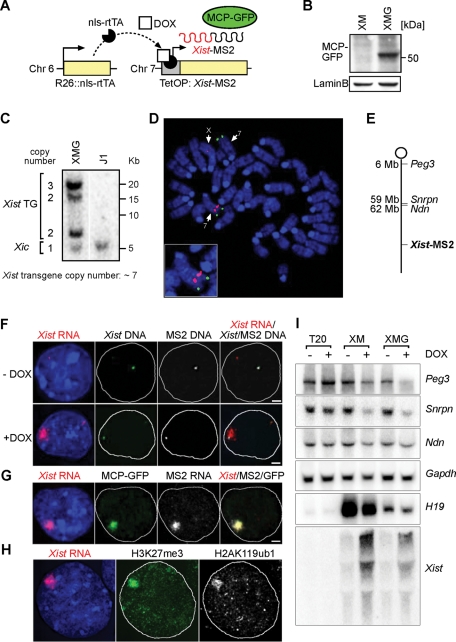
FIGURE 1:
Visualization of Xist in living XMG ES cells. (A) In XMG ES cells, expression of Xist-MS2 can be induced from a tetracycline-inducible promoter (TetOP) with Dox. The green fluorescent MCP-GFP RNA-binding protein is recruited to the MS2 sequences on the 3´ end of Xist-MS2. (B) Western analysis detects MCP-GFP expression in nuclear extracts from XMG ES cells. Lamin B is a loading control. (C) Southern analysis of XMG ES cells using the XB1K probe specific for Xist exon 1. Band intensities were quantified relative to the endogenous Xist gene in the Xic. An estimate of seven transgene copies is calculated. (D) Mapping of the Xist-MS2 transgene integration site to chromosome 7. A DNA FISH experiment on a metaphase spread from XMG ES cells using an Xist probe recognizing the endogenous Xist locus and transgene (red) and an Igf2/H19 BAC (RP23-50N22) FISH probe identifying chromosome 7 (green) is shown. (E) A map of the transgenic chromosome 7 in XMG ES cells. (F) Sequential RNA/DNA FISH of XMG ES cells using probes specific for Xist RNA (red), Xist DNA (green), and MS2 DNA (white) after 2 d of Dox addition (+DOX) or without induction (−DOX). Nucleus is stained with DAPI (blue). Scale bar, 2 μm. (G) Colocalization of GFP signal with Xist RNA demonstrated by combined GFP immunofluorescence and RNA FISH detecting MS2 (white) and Xist (red) in XMG ES cells 2 d after Dox addition. Scale bars, 2 μm. (H) Transgenic Xist expression induces histone modifications in XMG ES cells. Combined immunofluorescence RNA FISH analysis shows colocalization of H3K27me3 (green), H2AK119ub1 (white), and Xist RNA (red) in XMG ES cells after 2 d of Dox addition. (I) Xist expression in XM and XMG cells causes gene silencing on chromosome 7. Northern analysis of Xist and the imprinted and paternally expressed genes Peg3, Snrpn, and Ndn in control T20 (Schoeftner et al., 2006), XM, and XMG cells differentiated for 4 d in the presence (+) and absence (−) of Dox. The maternally expressed imprinted H19 gene is not repressed upon Xist induction but is expressed at variable levels in different ES cell lines. Gapdh is a loading control.