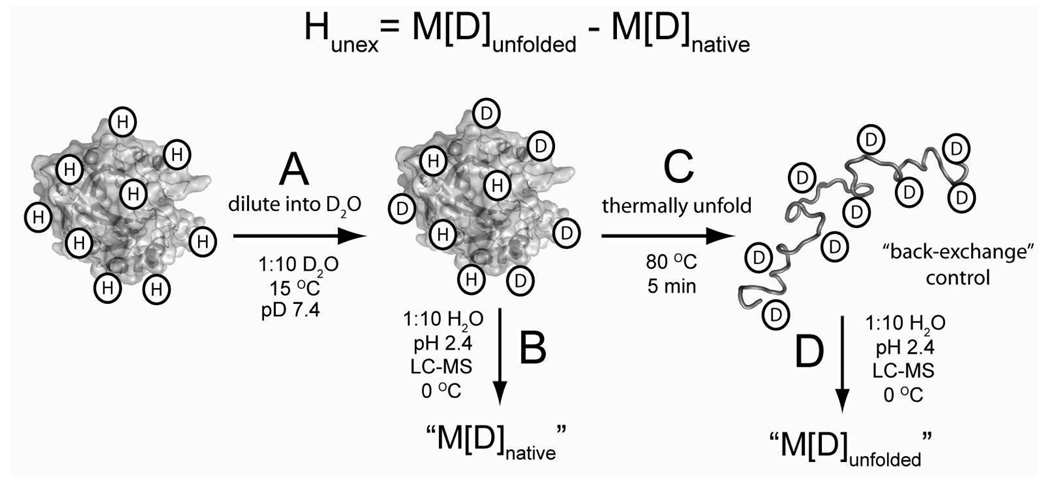
Figure 3. Measuring the amide hydrogen-deuterium exchange of proteins using liquid chromatography electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (LC-ESI-MS).
A) H/D exchange was initiated by diluting concentrated protein solutions (1:10 v/v) from buffered H2O into buffered D2O. B) The mass of the protein was measured as a function of time by quenching the isotopic exchange of an aliquot with low pH buffer (pH 2.4, 100 mM PO43−) and injection onto an LC-ESI-MS apparatus that was equilibrated at 0 °C (he ionization solvent used in LC-ESI-MS is 0.3 % formic acid, 49.85 % acetonitrile and 49.85 % H2O). We refer to this measured mass as M[D]native. C) The perdeuterated protein is prepared by thermally unfolding an aliquot from B and measuring the mass. We refer to this measured mass as M[D]unfolded. Deuterons on side chain functionalities (OH, -COOH, -NH3+, -C(NH2)2+) rapidly exchanged with H2O during the analysis with HPLC-MS (e.g., during steps “B” and “D”) and cannot be measured with this method. The number of unexchanged amide hydrogen (Hunex) at any given time during the experiment is calculated as Hunex = M[D]unfolded – M[D]native.