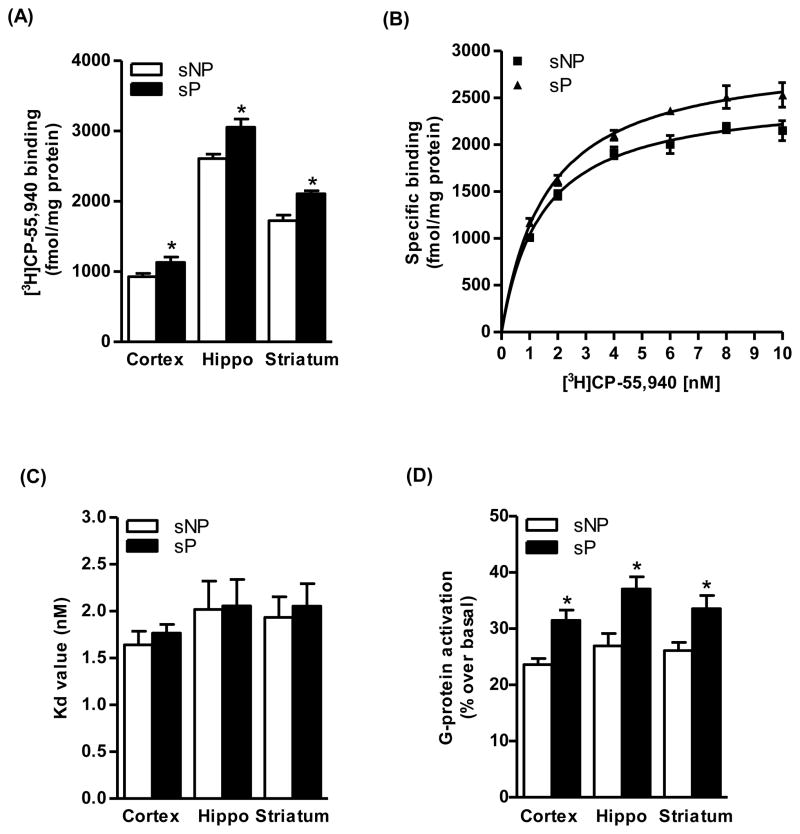
Figure 1.
Saturation analysis of [3H]CP-55,940 binding indicated a higher Bmax values in the cerebral cortex (22%, p<0.05), hippocampus (18%, p<0.05) and striatum (22%, p<0.05) of alcohol-naive sP than sNP rats (A). A representative graph of saturation isotherm of [3H]CP-55,940 binding to hippocampal membranes is shown in figure B. There were no significant differences in Kd values of the receptor for the radioligand between the groups (C). Basal levels CB1 receptor-mediated G-protein coupling were found to be higher in the cerebral cortex (33%, p<0.05), hippocampus (38%, p<0.01) and striatum (29%, p<0.05) of alcohol-naive sP than sNP rats (D).