Figure 1.
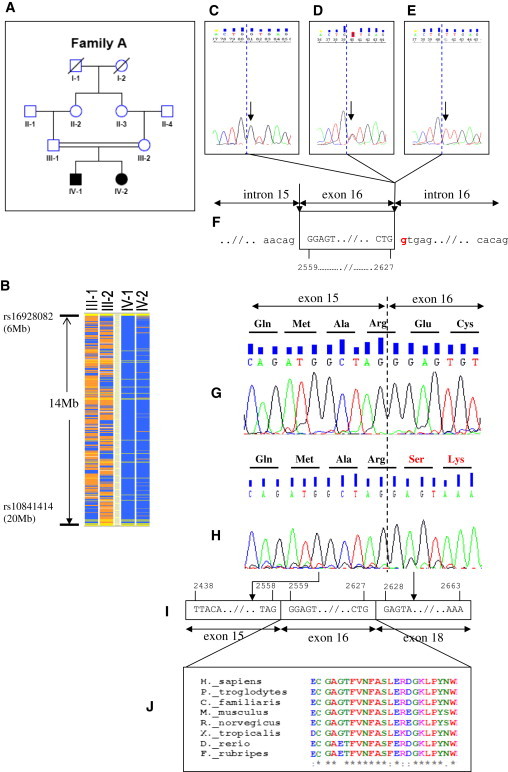
Positional Cloning of PTPRO Mutations in Family A
(A) The pedigree of the index family. Squares indicate males and circles indicate females. Solid symbols indicate affected individuals. Double-horizontal bars indicate consanguinity.
(B) The schematic representation of homozygosity data. Genotype files (CHP files) were generated with Affymetrix GTYPE software and were transferred to the VIGENOS (Visual Genome Studio) program (Hemosoft, Ankara),13 which facilitates visualization of a large quantity of genomic data in comprehensible visual screens. Homozygous genotypes identical to the genotype data obtained from the index case (IV-1) are shown in blue. Contrasting homozygote genotypes are shown in white, whereas heterozygous SNPs appear in orange. Noninformativeness as a result of heterozygous genotypes in parent-child trios is indicated in yellow. No calls are indicated in gray. The overlapping homozygous stretches in two affected individuals are approximately 14 Mb in size between markers rs16928082 and rs10841414 on chromosome 12.
(C–E) The sequence electropherograms of exon 16 of PTPRO. The wild-type sequence in a healthy control is shown in the left electropherogram (C, arrow). Whereas the healthy parents were heterozygous for the mutation (D, arrow), both affected siblings had a homozygous donor splice-site c.2627+1G>T (p.Glu854_Trp876del) mutation (E, arrow); dashed blue lines show exon-intron boundaries.
(F) The position of the mutation is shown as red in the genomic sequence. Horizontal arrows indicate subsequent introns and exons. Vertical arrows show intron-exon boundaries. Four-digit numbers (i.e., 2559 and 2627) show starting and ending nucleotides of exon 16.
(G) Sequencing of PTPRO cDNA of both peripheral blood lymphoctes from healthy individuals and nephrectomy specimens showed that exon 15 was followed by exon 16 (normal splicing). Dashed line shows exon-exon boundaries.
(H–J) c.2627+1G>T donor splice-site mutation (NM_002848.2) in Family A results in skipping of exon 16, which is conserved during evolution (see also Figure S3). Four-digit numbers show start and end positions of the respective exons.
