Abstract
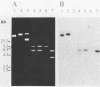
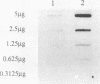
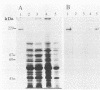
A recombinant Streptococcus lactis strain which carries the structural gene for a surface protein antigen (PAc) of 190,000 daltons from Streptococcus mutans serotype c was constructed for development of an oral vaccine against dental caries. The gene from S. mutans MT8148 joined to shuttle vector pSA3 was successfully transformed into S. lactis IL1403. A small amount of PAc was detected in the cell homogenate and cytoplasmic fraction of the recombinant S. lactis, but not in the culture supernatant of the recombinant, by Western immunoblotting and dot immunoblotting. The level of PAc-specific mRNA in the recombinant strain was lower than that in S. mutans MT8148. However, significant salivary immunoglobulin A and serum immunoglobulin G responses to PAc were induced in mice immunized orally with the recombinant S. lactis.
Full text
PDF


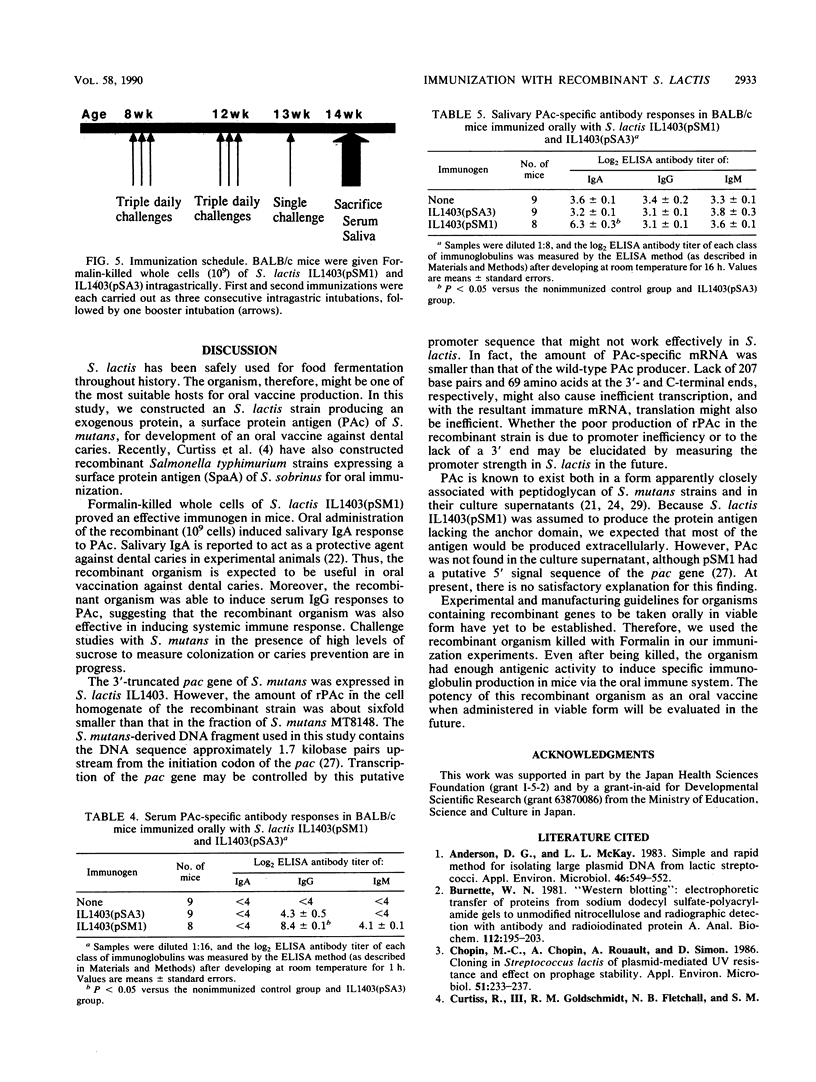

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson D. G., McKay L. L. Simple and rapid method for isolating large plasmid DNA from lactic streptococci. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Sep;46(3):549–552. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.3.549-552.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chopin M. C., Chopin A., Rouault A., Simon D. Cloning in Streptococcus lactis of plasmid-mediated UV resistance and effect on prophage stability. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Feb;51(2):233–237. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.2.233-237.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtiss R., 3rd, Goldschmidt R. M., Fletchall N. B., Kelly S. M. Avirulent Salmonella typhimurium delta cya delta crp oral vaccine strains expressing a streptococcal colonization and virulence antigen. Vaccine. 1988 Apr;6(2):155–160. doi: 10.1016/s0264-410x(88)80020-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dao M. L., Ferretti J. J. Streptococcus-Escherichia coli shuttle vector pSA3 and its use in the cloning of streptococcal genes. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Jan;49(1):115–119. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.1.115-119.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forester H., Hunter N., Knox K. W. Characteristics of a high molecular weight extracellular protein of Streptococcus mutans. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Sep;129(9):2779–2788. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-9-2779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada S., Slade H. D. Biology, immunology, and cariogenicity of Streptococcus mutans. Microbiol Rev. 1980 Jun;44(2):331–384. doi: 10.1128/mr.44.2.331-384.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt R. G., Abiko Y., Saito S., Smorawinska M., Hansen J. B., Curtiss R., 3rd Streptococcus mutans genes that code for extracellular proteins in Escherichia coli K-12. Infect Immun. 1982 Oct;38(1):147–156. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.1.147-156.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes M., Machardy S. M., Sheppard A. J., Woods N. C. Evidence for an immunological relationship between Streptococcus mutans and human cardiac tissue. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):576–588. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.576-588.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klaenhammer T. R., Sanozky R. B. Conjugal transfer from Streptococcus lactis ME2 of plasmids encoding phage resistance, nisin resistance and lactose-fermenting ability: evidence for a high-frequency conjugative plasmid responsible for abortive infection of virulent bacteriophage. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Jun;131(6):1531–1541. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-6-1531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo J. K., McKay L. L. Plasmid transformation of Streptococcus lactis protoplasts: optimization and use in molecular cloning. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Aug;48(2):252–259. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.2.252-259.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. F., Progulske-Fox A., Bleiweis A. S. Molecular cloning and expression of a Streptococcus mutans major surface protein antigen, P1 (I/II), in Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1988 Aug;56(8):2114–2119. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.8.2114-2119.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehner T., Caldwell J., Smith R. Local passive immunization by monoclonal antibodies against streptococcal antigen I/II in the prevention of dental caries. Infect Immun. 1985 Dec;50(3):796–799. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.3.796-799.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehner T. Immunization against dental caries. Vaccine. 1985 Mar;3(1):65–68. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(85)90016-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehner T., Russell M. W., Caldwell J., Smith R. Immunization with purified protein antigens from Streptococcus mutans against dental caries in rhesus monkeys. Infect Immun. 1981 Nov;34(2):407–415. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.2.407-415.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loesche W. J. Role of Streptococcus mutans in human dental decay. Microbiol Rev. 1986 Dec;50(4):353–380. doi: 10.1128/mr.50.4.353-380.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma J. K., Smith R., Lehner T. Use of monoclonal antibodies in local passive immunization to prevent colonization of human teeth by Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1987 May;55(5):1274–1278. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.5.1274-1278.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBride B. C., Song M., Krasse B., Olsson J. Biochemical and immunological differences between hydrophobic and hydrophilic strains of Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1984 Apr;44(1):68–75. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.1.68-75.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morisaki I., Michalek S. M., Harmon C. C., Torii M., Hamada S., McGhee J. R. Effective immunity to dental caries: enhancement of salivary anti-Streptococcus mutans antibody responses with oral adjuvants. Infect Immun. 1983 May;40(2):577–591. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.2.577-591.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogundipe J. O., Holt R. G. Molecular and immunochemical characterization of recombinant Escherichia coli containing the spaA gene region of Streptococcus sobrinus. Infect Immun. 1989 Jul;57(7):1906–1915. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.7.1906-1915.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohta H., Kato H., Okahashi N., Takahashi I., Hamada S., Koga T. Characterization of a cell-surface protein antigen of hydrophilic Streptococcus mutans strain GS-5. J Gen Microbiol. 1989 Apr;135(4):981–988. doi: 10.1099/00221287-135-4-981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okahashi N., Koga T., Hamada S. Purification and immunochemical properties of a protein antigen from serotype g Streptococcus mutans. Microbiol Immunol. 1986;30(1):35–47. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1986.tb00919.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okahashi N., Sasakawa C., Yoshikawa M., Hamada S., Koga T. Cloning of a surface protein antigen gene from serotype c Streptococcus mutans. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Feb;3(2):221–228. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb01811.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okahashi N., Sasakawa C., Yoshikawa M., Hamada S., Koga T. Molecular characterization of a surface protein antigen gene from serotype c Streptococcus mutans, implicated in dental caries. Mol Microbiol. 1989 May;3(5):673–678. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00215.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell M. W., Bergmeier L. A., Zanders E. D., Lehner T. Protein antigens of Streptococcus mutans: purification and properties of a double antigen and its protease-resistant component. Infect Immun. 1980 May;28(2):486–493. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.2.486-493.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell R. R. Wall-associated protein antigens of Streptococcus mutans. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Sep;114(1):109–115. doi: 10.1099/00221287-114-1-109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon D., Rouault A., Chopin M. C. High-efficiency transformation of Streptococcus lactis protoplasts by plasmid DNA. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Aug;52(2):394–395. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.2.394-395.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi I., Okahashi N., Sasakawa C., Yoshikawa M., Hamada S., Koga T. Homology between surface protein antigen genes of Streptococcus sobrinus and Streptococcus mutans. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jun 5;249(2):383–388. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80664-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terzaghi B. E., Sandine W. E. Improved medium for lactic streptococci and their bacteriophages. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Jun;29(6):807–813. doi: 10.1128/am.29.6.807-813.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA transferred or dotted nitrocellulose paper. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:255–266. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00060-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Vossen J. M., Kok J., Venema G. Construction of cloning, promoter-screening, and terminator-screening shuttle vectors for Bacillus subtilis and Streptococcus lactis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Aug;50(2):540–542. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.2.540-542.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]