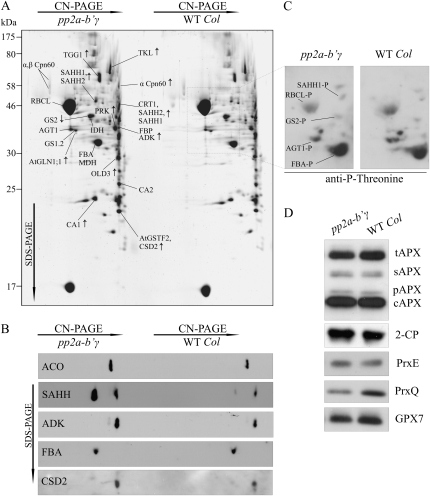
Figure 4.
Proteomic analysis of pp2a-b′γ leaves. A, Representative SYPRO-stained 2D gel depicting proteins in the total foliar soluble fractions isolated from pp2a-b′γ and wild-type (WT Col) plants. Oligomeric complexes were separated by CN-PAGE followed by SDS-PAGE in the second dimension. The proteins were identified by in-gel trypsin digestion and subsequent analysis by nano-HPLC electrospray ionization-quadrupole-time-of-flight MS/MS. Protein spots showing higher or lower intensity in pp2a-b′γ as compared with the wild type are indicated by arrows. Details concerning the identified proteins and phosphopeptides are presented in Table II. B, Immunoblots of 2D gels demonstrating increased steady-state levels of ACO, SAHH (isoforms 1 and 2 in both of the spots), ADK, and CSD2 in the pp2a-b′γ mutant as compared with wild-type plants. Fru bisphosphate aldolase (FBA) is shown as a control, as it showed no differences between the lines. C, Phosphoproteins of pp2a-b′γ and wild-type soluble leaf extracts as detected from 2D CN-PAGE by immunoblotting with anti-P-Thr antibody. The phosphoproteins were identified based on relative locations to Rubisco subunits on the gel and on the presence of phosphopeptides in the MS/MS spectra as presented in Table II. The corresponding area on a SYPRO-stained 2D gel is indicated with a box in A. D, Steady-state levels of antioxidant enzymes in pp2a-b′γ mutant and wild-type plants. tAPX, Thylakoid ascorbate peroxidase (APX); sAPX, stromal APX; pAPX, peroxisomal APX; cAPX, cytoplasmic APX; 2-CP, chloroplastic 2-Cys peroxiredoxins A and B; PrxE, peroxiredoxin IIE; PrxQ, peroxiredoxin Q; GPX7, glutathione peroxidase 7.