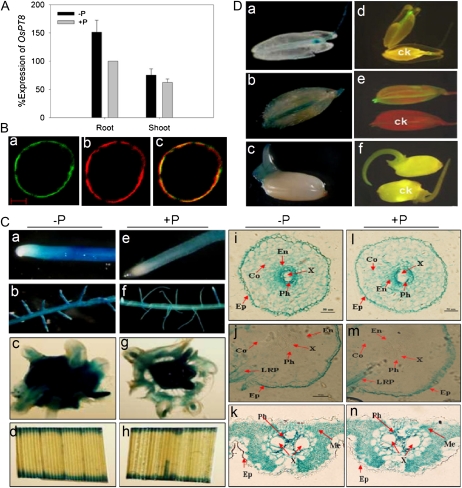
Figure 1.
Expression pattern in response to Pi availability, and subcellular and tissue localization analysis of OsPT8. A, Detection of the expression level of OsPT8 in wild-type plants by analysis. Total RNA was extracted from rice plants grown for 21 d in the nutrient solution with 0.3 mm Pi (HP; +P) or 0.015 mm Pi (LP; −P). PCR were performed with specific primers for OsPT8 (Supplemental Tables S1 and S2). The expression of OsActin was used as an internal control. B, Expression of cauliflower mosaic virus 35S promoter::OsPT8::GFP fusion genes in rice protoplast. a, Confocal image of the protoplast under the GFP channel showing the plasma membrane localization of 35S::OsPT8::GFP. b, The red fluorescence reflects the position of the plasma membrane, as indicated by the plasma membrane-specific dye 1007PM-rk. c, The merged image of a and b. Bar = 100 nm. C, GUS staining observation of transgenic rice plants harboring the OsPT8 promoter::GUS fusion. Expression is shown in different tissues of rice supplied with 0.3 mm Pi (HP; +P [e–h]) or 0.015 mm Pi (LP; −P [a–d]) for 21 d. a and e, Root tip. b and f, Lateral root branching zone. c and g, Hand-cut cross sections of the root-shoot junction. d and h, Leaf blade. i and l, Root tip cross sections of Pi-deficient (i) and Pi-sufficient (l) plants showing GUS activity in the epidermis (Ep), cortex (Co), endodermis (En), phloem (Ph), and xylem (X). j and m, Cross sections of the lateral root branching zone of Pi-deficient (j) and Pi-sufficient (m) plants showing GUS activity only in the phloem, xylem, and lateral root primordium (LRP). k and n, Cross sections of leaf blade from Pi-deficient (k) and Pi-sufficient (n) plants. Leaf cell types showing GUS expression include the phloem, xylem, and mesophyll (Me) cells. D, Tissue localization of OsPT8 promoter::GUS and OsPT8 promoter::GFP expression in stamens (a and d), caryopsis (b and e), and 3-d-old germinated seeds (c and f) of Pi-sufficient plants. ck, Stamens (d), caryopsis (e), and germinated seeds (f) of wild-type plants.