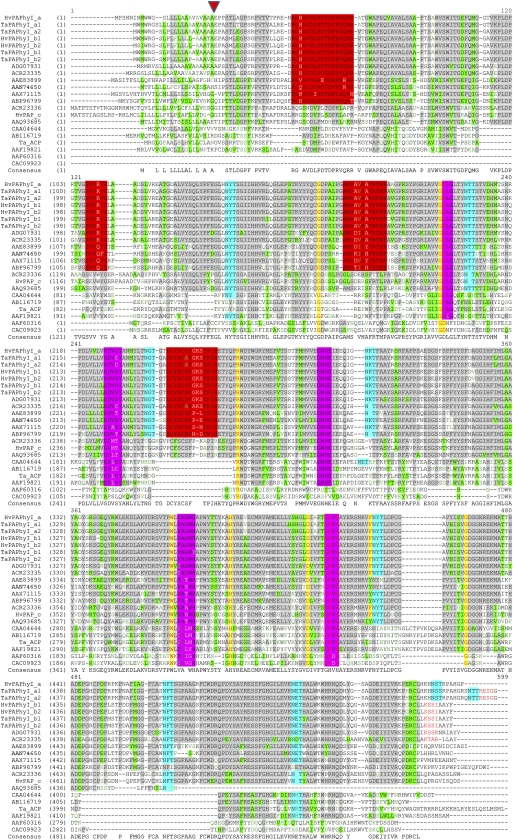
Figure 2.
Multiple alignments (ClustalW) of selected PAPs with or without known phytase activity. Gray shading, partial similarity; yellow shading, full similarity; green shading, weak similarity; purple-pink shading, PAP motifs; red shading, predicted PAPhy motifs; red letters, potential C-terminal ER-retention signals; cyan shading, potential N-linked glycosylation sites. The alignment includes all PAPhys represented in Figure 1 and at least two representatives from each of the five PAP types. A predicted signal peptide cleavage site is indicated by an arrowhead approximately 20 amino acids from the N termini for some of the PAPs. GenBank protein accession numbers are as follows: HvPAPhy_a, ACR23331; TaPAPhy_a1, ACR23326; TaPAPhy_a2, ACR23327; HvPAPhy_b1, ACR23332; HvPAPhy_b2, ACR23333; TaPAPhy_b1, ACR23328; TaPAPhy_b2, ACR23329; rice PAPhy_b, ADG07931; maize PAPhy_b, ACR23335; soybean PAPhy_b, AAE83899; Arabidopsis PAP15, AAN74650; M. truncatula PAPhy, AAX71115; Nicotiana tabacum PAPhy, ABP96799; maize PAP_c (type IV), ACR23336; HvPAP_c, ACR23334; Arabidopsis PAP_c (type IV), AAQ93685; kidney bean PAP group type III, CAA04644; kidney bean PAP type IV, AB116719; Ta_ACP, ACR23330; Ipomoea batatas PAP group type III, AAF19821; soybean PAP type V, AAF60316; Arabidopsis PAP type V, CAC09923.