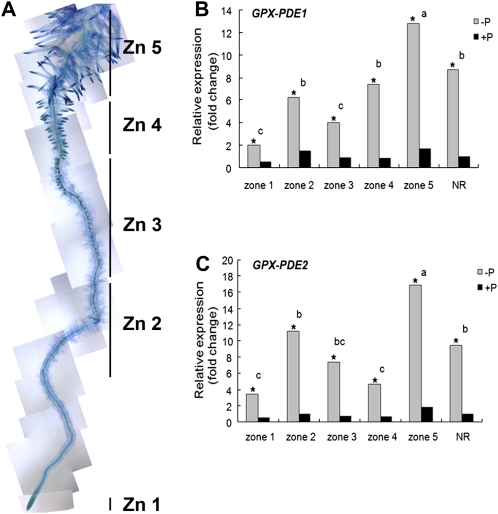
Figure 2.
Cluster root development and qRT-PCR analysis of GPX-PDE expression in cluster roots of white lupin grown under Pi-sufficient and Pi-deficient conditions. A, Lupin cluster roots from Pi-deficient and Pi-sufficient plants can be separated into five zones (Zn): zone 1, root tip; zone 2, early meristems; zone 3, unemerged rootlets; zone 4, newly emerged and juvenile rootlets; zone 5, mature cluster roots covered with abundant root hairs (Neumann et al., 1999). Note that cluster roots can form on Pi-sufficient plants but constitute 10% or less of the root mass. However, on Pi-deficient plants, they constitute greater than 60% of the root mass (Johnson et al., 1994, 1996). B and C, Relative expression of white lupin GPX-PDE1 and GPX-PDE2 in the five developmental zones of Pi-deficient and Pi-sufficient cluster roots. qRT-PCR is shown for first-strand cDNA generated from Pi-sufficient (+P) and Pi-deficient (−P) lupin cluster root zones and normal roots (NR) using specific primer pairs for GPX-PDE1 and GPX-PDE2. Data are expressed as relative values based on the GPX-PDE1 or GPX-PDE2 expression level in +P normal roots and referenced as 1.0. Lowercase letters denote significant differences between zones (P ≤ 0.05). Asterisks denote significant differences between –P and +P (P ≤ 0.05). Statistical significance was based on three biological replicates.