Figure 1. Cloning and Subcellular Localization of ApNLG.
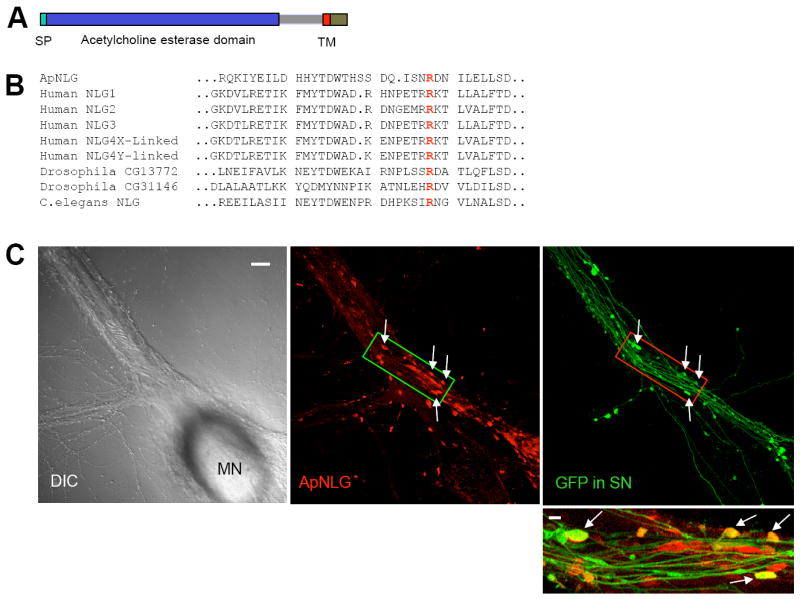
(A) The domain structure of ApNLG is similar to vertebrate neuroligin. SP= signal peptide. TM=transmembrane domain. (B) Comparison of the deduced amino acid sequence of ApNLG (partial) with vertebrate and invertebrate homologs. A highly conserved arginine (R) residue that is mutated in human NLG-3 R451C linked to ASD is present in the ApNLG (bold red). (C) Left: A DIC image shows a sensory-to-motor neuron co-culture. MN denotes the motor neuron cell body. Sensory neuron cell body is located outside of the field of view. Middle: ApNLG immunostaining (red) shows clustering of ApNLG at the initial segment and proximal regions of the major axons of the postsynaptic motor neuron. Right: GFP (green) as a whole cell marker outlines presynaptic sensory neuron processes and varicosities. Scale bar 20 μm. Bottom: A merged image in a magnified view shows some sensory neuron varicosities that partially or completely overlap with ApNLG clusters (yellow, arrows). Magnified view, scale bar 5 μm.
See also Figure S1 and S2.
