Figure 6. ApNRX Mediates LTF and Associated Presynaptic Structural Changes.
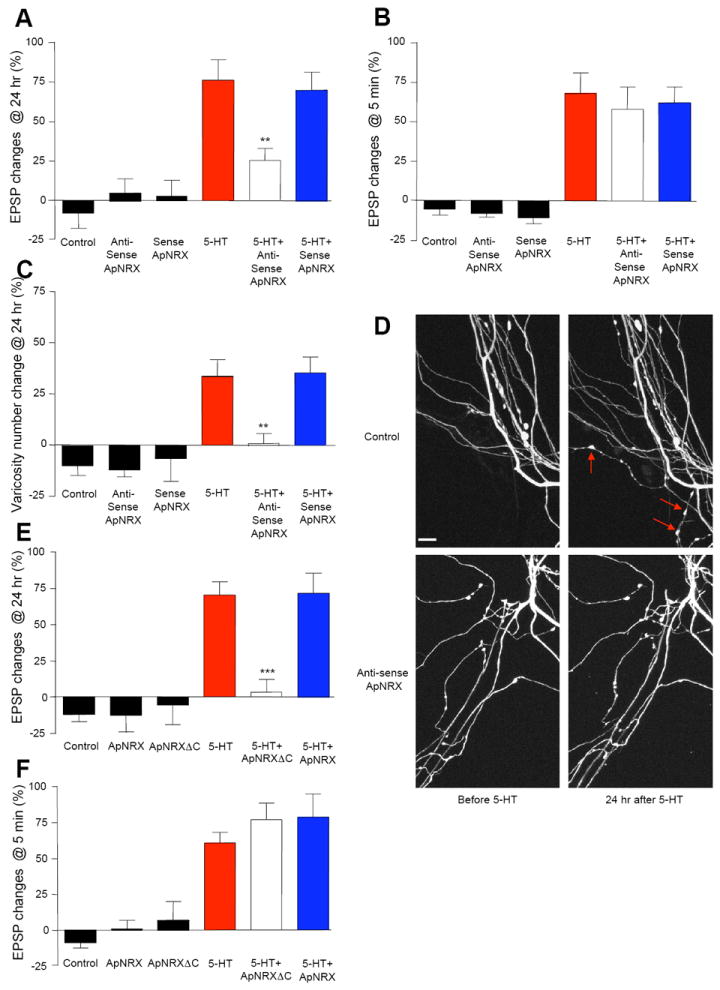
(A and B) Injection of ApNRX anti-sense oligonucleotide into the presynaptic sensory neuron to down-regulate the translation levels of ApNRX blocks LTF (A) but has no effect on STF (B). EPSPs were recorded from motor neurons in response to extracellular stimulation of sensory neurons before and 24 hr after exposure to 5 × 5-HT (10 μM, 5 min) for LTF or before and 5 min after exposure to 1 × 5-HT (10 μM, 5 min) for STF. Changes in amplitudes are shown as a bar graph. (C) Injection of ApNRX anti-sense oligonucleotide in the presynaptic sensory neuron also blocks growth of new presynaptic varicosities associated with LTF. The sensory neurons were injected a whole cell marker Alexa 594. The number of sensory neuron varicosities in apposition to the initial segment and major neuritis of motor neuron were counted before and 24 hours after exposure to 5 × 5-HT (10 μM, 5 min). Changes in numbers of varicosities are shown as a bar graph. Total of 65 cells and 803 varicosities in 11 independent experiments were analyzed. (D) Representative images of presynaptic varicosities before and after 5-HT treatment. Red arrows indicate some newly formed varicosities. Scale bar 10 μm. (E and F) Expression of ApNRXΔC in the presynaptic sensory neuron blocks LTF (E) but has no effect on STF (F). EPSPs were recorded from motor neurons in response to extracellular stimulation of sensory neurons before and 24 hr after exposure to 5 × 5-HT (10 μM, 5 min) for LTF or before and 5 min after exposure to 1 × 5-HT (10 μM, 5 min) for STF. Changes in amplitudes are shown as a bar graph.
See also Figure S3.
