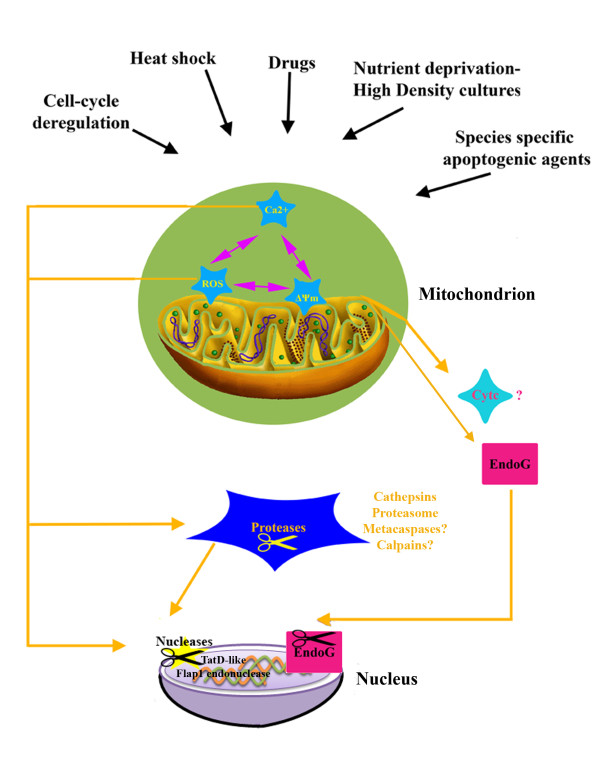
Figure 1.
Representation of the major pathways leading to apoptosis in trypanosomatids. The different triggers of apoptosis result in the loss of mitochondrial membrane potential (ΔΨm), the generation of reactive oxygen species formation (ROS) and increase in cytosolic Ca2+ (Ca2+). These changes potentiate the release of cytochome c and EndoG into the cytoplasm and the activation of proteases and nucleases to dismantle the parasites in an ordered fashion. Upon release from the mitochondrion EndoG translocates to the nucleus to degrade DNA. The question marks (?) represent a function that either awaits confirmation in trypanosomatids or that has been suggested for only some genera of trypanosomatids.