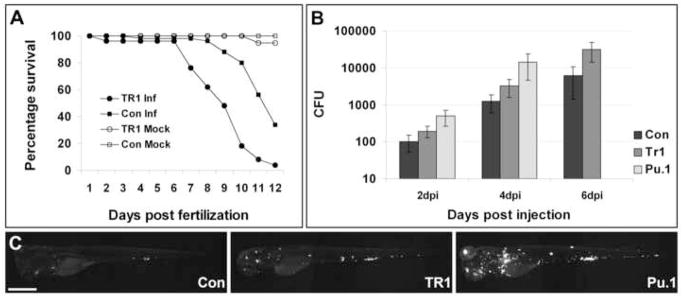
Figure 1.
TR1 morphant embryos are more susceptible to mycobacterial infection. (A) Control (Con) and TR1 morphant embryos were either mock injected (n=30 each) or infected with 108 +/- 11 colony forming units (CFU) of M. marinum on 1 dpf (n=50 each). Data are plotted as percentage of surviving embryos on each day. TR1 morphant embryos are significantly more susceptible to infection with M. marinum than controls (Hazard ratio 5.7, p < 0.0001, Kaplan Meier method with log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test). Survival was not statistically different between mock-injected TR1 and control embryos. (B) Mean bacterial loads per embryo for control (Con), TR1, and Pu.1 morphant embryos at 2, 4, and 6 days post injection (dpi) with 70 ± 13 CFU. p < 0.0001 by 1-way ANOVA. Data for Pu.1 embryos are only available for 2 and 4 dpi due to mortality. Error bars represent standard deviation from the mean. All morphant bacterial loads are significantly different from each other (p<0.05) at each individual time points (Control versus TR1, Control versus Pu.1, and TR1 versus Pu.1) by Student’s unpaired t-test. (C) Representative pictures of control, TR1, and Pu.1 morphant embryos at 4 dpi with fluorescence representing bacterial load. Scale bar, 500 μm.