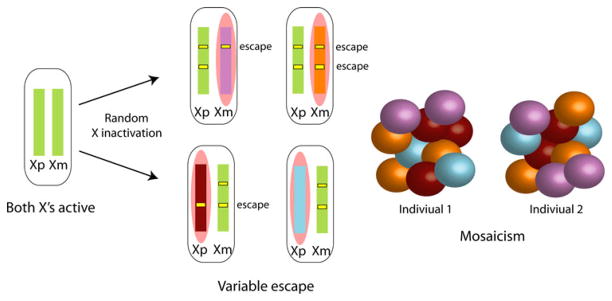
Fig. 1.
X inactivation and escape patterns. Before differentiation, the paternal X (Xp) and the maternal X (Xm) chromosomes are active. As cells differentiate, random X inactivation is initiated by coating one X chromosome with Xist RNA (pink cloud). This will become the inactive X, while the other X remains active (green chromosome). Since the process is random, either the Xp or the Xm is inactivated in a given cell, resulting in mosaicism in females. Some genes escape X inactivation, i.e., are expressed from both the Xi and the Xa (yellow bars) in all cells. Other genes escape from X inactivation in a subset of cells in a given tissue resulting in mosaicism of escape patterns. An additional layer of variability in escape patterns results from differences between individuals (Carrel and Willard 2005; Yang et al. 2010)