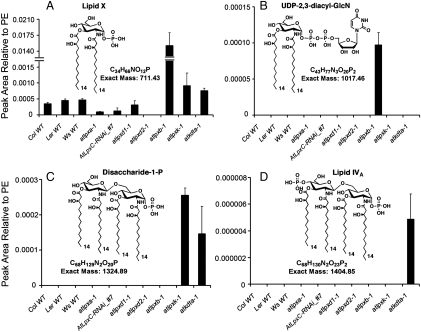
Fig. 4.
Quantification of 2,3-diacylglucosamine 1-phosphate and other lipid A precursors in Arabidopsis mutants. MRM analysis and quantification of 2,3-diacylglucosamine 1-phosphate (lipid X) (A), UDP-2,3-diacyl-GlcN (B), disaccharide 1-phosphate (C), and lipid IVA (D) was carried out using lipids extracted from the indicated 10-day old seedlings of three parental wild types, six Arabidopsis insertional mutants, and one RNAi transgenic line. These Arabidopsis lipid A precursors, which have the same acyl chain compositions and molecular weights as their E. coli counterparts (Fig. 1), were detected using the precursor/product ion pairs shown in Fig. S3. Peak areas were normalized to the major phosphatidylethanolamine molecular species (C16∶0/C18∶2) present in the same sample (Fig. S3). Error bars represent standard deviations of three biological replicates. The full LC–MRM tracings for each precursor/product ion pair are shown in Figs. S4, S6, S7, and S8. All LC–MRM experiments were performed using a 4,000 Q-Trap hybrid triple quadrupole linear ion trap mass spectrometer, equipped with a Turbo V ion source (Applied Biosystems).