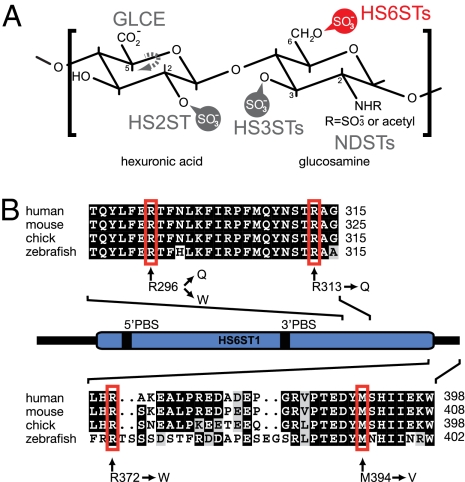
Fig. 1.
Function and sequence of human HS6ST1 and positions of amino acids mutated in patients with IHH. (A) Characteristic disaccharide of HS consisting of a hexuronic acid and a glucosamine residue. The positions within the HS sugars that can be modified by HS-modifying enzymes are indicated. Vertebrate genomes encode a single HS C-5 glucuronyl epimerase (GLCE) and HS 2-O-sulfotransferase (HS2ST) as well as at least three, four, or seven HS 6-O-sulfotransferases (HS6STs, indicated in red), N-deacetylase/sulfotransferases (NDSTs), or HS 3-O-sulfotransferases (HS3STs), respectively (5). (B) Schematic representation of the human HS6ST1 protein with the conserved sulfotransferase domain indicated in blue. 5′PBS and 3′PBS indicate the phosphoadenosyl-phosphosulfate (PAPS) cofactor binding sites. A multiple sequence alignment of two sections of the C terminus is shown with nonsynonymous changes indicated and amino acid positions denoted on the right. Amino acids shaded in black and gray indicate identical and similar residues, respectively.