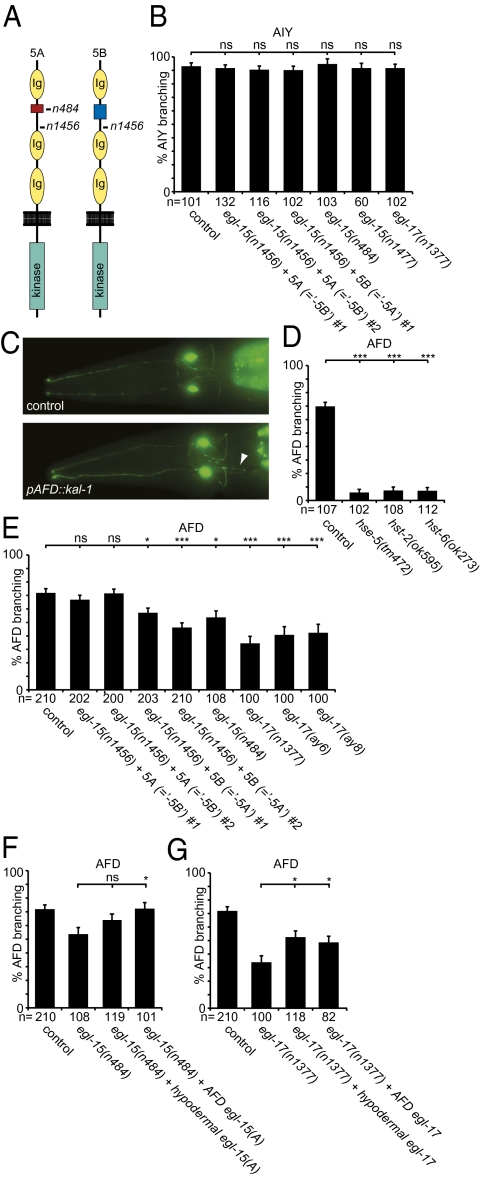
Fig. 3.
kal-1 function requires hst-6, FGFR/egl-15, and FGF/egl-17. (A) Schematic of the two FGFR/EGL-15 extracellular splice variants 5A and 5B, which differ by a short sequence between Ig domains 1 and 2 indicated in blue and red. The nonsense alleles n484 and n1456 produce premature stop codons in 5A-specific or all splice variants, respectively. The n1456 allele results in complete loss of function. (B) Quantification of kal-1–dependent axonal branching in AIY interneurons in different mutant backgrounds. Indicated are transgenic lines (#1 = otEx1262, #2 = otEx1266 for the “-5B” strains and #1 = otEx1254 for the “-5A” strain) that exclusively express the egl-15(5A) or egl-15(5B) splice variant, respectively, in an egl-15(n1456) null mutant background (26). The egl-15(n484) allele is an egl-15(5A)–specific null allele (43), egl-15(n1477) is a strong temperature-sensitive allele, and egl-17(n1377) is a null allele (27). (C) Ventral view of the pair of AFD sensory interneurons (anterior is to the left). A kal-1–dependent axonal branch (otIs83) (15) is indicated (Lower, arrowhead) that is not observed in WT animals (Upper). (D) kal-1–dependent branching phenotype in AFD sensory neurons (otIs83) is suppressed by loss of the HS C-5 epimerase (hse-5), hst-2, or hst-6. (E) The kal-1–dependent branching phenotype in AFD sensory neurons (otIs83) is suppressed by loss of the FGFR/egl-15(5A) variant or the FGF/egl-17 ligand [using three null alleles: egl-17(n1377), egl-17(ay6), and egl-17(ay8)] (27). Indicated are transgenic lines (#1 = otEx1262, #2 = otEx1266 for the “-5B” strains and #1 = otEx1254, #2 = otEx1255 for the “-5A” strain) that exclusively express the egl-15(5A) or egl-15(5B) splice variant, respectively, in an egl-15(n1456) null mutant background (26). (F) Suppression of the kal-1–dependent branching phenotype in AFD sensory neurons by loss of the FGF receptor egl-15 is rescued by expression of FGFR/egl-15 specifically in AFD neurons (dzEx480, using the gcy-8 promoter) (42) but not in the hypodermis (dzEx484, using the dpy-7 promoter) (41). (G) Suppression of kal-1–dependent branching in AFD sensory neurons by loss of the FGF ligand egl-17 is partially rescued by expression of FGF/egl-17 in the hypodermis (dzEx472, using the dpy-7 promoter) (41) or in AFD neurons (dzEx483, using the gcy-8 promoter) (41). Representative transgenic lines are shown in F and G (for additional transgenic lines see Fig. S3).