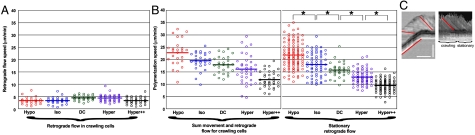
Fig. 3.
The effect of membrane tension on retrograde flow and apparent polymerization rates. (A) Dot plots of speeds of retrograde flow (absolute values) during cell translocation. Red: hypotonic medium (130 mOsm); blue: isotonic media (175 mOsm); green: 150 μm DC; purple: hypertonic media (275 mOsm); black: strong hypertonic media (350 mOsm). (B) Polymerization speed under conditions as in A. (Left) Movement plus retrograde flow speeds (absolute values) for crawling cells. (Right) Retrograde flow speeds of stationary cells (absolute values). All differences in stationary retrograde flow values are significant (marked with an asterisk). The sum values give the same trend as the stationary retrograde flow values. (C) Transmitted light kymograph of a representative cell that transitions between translocating and stationary behaviors. [Features observable by transmitted light correspond to fluorescent MSP structures and show comparable dynamics (Fig. S2).] (Left) Normal kymograph, (Right) kymograph taken from the same cell but with the cell bodies aligned using a MatLab script. Example kymograph slopes drawn in red. Vertical scale bar = 5 μm, and horizontal scale bar = 15 s.