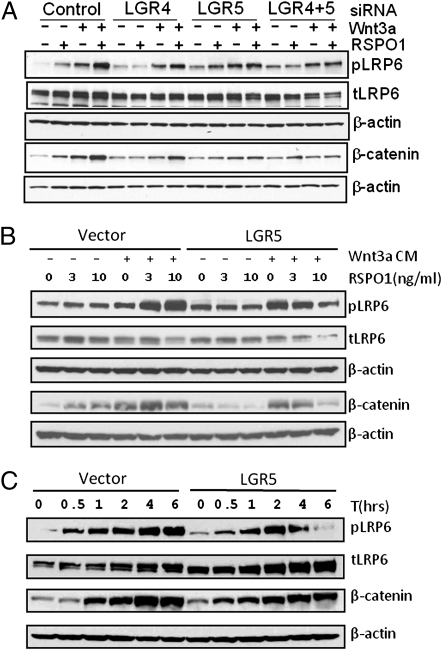
Fig. 5.
Effect of LGR4 and LGR5 expression knockdown and LGR5 overexpression on Wnt3a-RSPO1–induced LRP6 phosphorylation and β-catenin accumulation. (A) Effect of LGR4 and LGR5 expression knockdown on endogenous response to Wnt3a-RSPO1 in LRP6 phosphorylation and β-catenin levels. HEK293T cells were transfected with control, LGR4-, or LGR5-siRNA, or both, and 2 d later, the cells were stimulated with RSPO1 (4 nM), or Wnt3a (3 nM), or both for 3 h. Phospho-LRP6 at Ser1490 (pLRP6), total LRP6 (tLRP6), nonmembrane-associated β-catenin (membrane-bound β-catenin was removed with Con A-sepharose beads), and β-actin (loading control) were then probed by immunoblot analysis. (B) Change in pLRP6 and β-catenin levels in response to RSPO1 and Wnt3a treatment in vector and LGR5-overexpressing cells. HEK293 cells stably expressing vector or LGR5 were stimulated with RSPO1 (0, 3, and 10 ng/mL) with or without Wnt3a CM for 3 h, and probed as above. (C) Time course of LRP6 phosphorylation and changes in β-catenin levels following Wnt3a and RSPO1 treatment. The cells were stimulated with RSPO1 (100 ng/mL) and Wnt3a CM for 0–6 h and probed as above.